Skip over navigation
Article by Michael Grayling




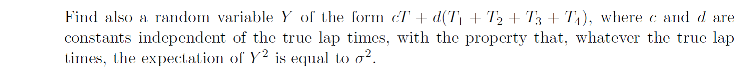
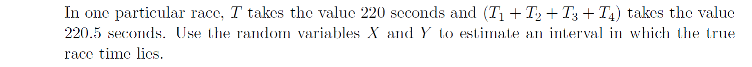

Well done if you've managed to complete any of these questions! If not, don't worry, mastering any topic in STEP can require a lot of practice. Fortunately, for Statistics questions in particular there is an abundance available and they're very easy to find: open any STEP past paper and turn to Section C and you should find something to challenge yourself with.
Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Age 16 to 18
Published 2014
STEP Stats Questions with Hints
Below you will find three relevant STEP Statistics questions for you to tackle. Don't worry, they come complete with a few hints to make things a little easier!
How much milk is in your cartons? (STEP Question 13 Paper I 2005)

How can you split up the required probabilities to use the given resuts and the symmetry property? What is the formula for conditional probabilties?

What probability do we need to compute? How can we split this up into factors for having bought either a full fat or skimmed carton? For each of the carton types, what range in terms of their means and standard deviations must we lie in 500 to 505 ml?

Can you use the new information and your result from the previous part to write down an equation relating \(a\) and \(b\)? What exact probability corresponds to the specified \( 1/3 \) of cartons? Can you compute what this probability is in terms of \(a\) and \(b\)?
Race times as random variables (STEP Question 12 Paper III 2005)

What can you say about the expected value of the sum of the \( T_i \)? What condition on \( a \) and \( b \) does point (1) give? What is the variance of the random variable in terms of just \( a \) and \( \sigma \)? How do you minimise a function like this?
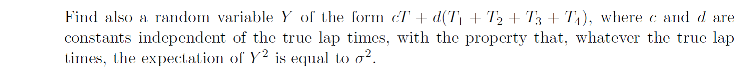
Using the formula for the variance of a random variable, how can we write \( \mathbb{E}(Y^2) \)? What condition on \(c\) and \(d\) do you get from independence of the true lap times? What about the expected value being \( \sigma^2 \)?
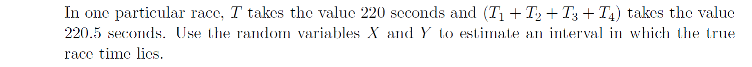
\( X \) and \( Y \) give you good estimates of the true race time and the variance respectively. How can you use this to form an interval for the race time?
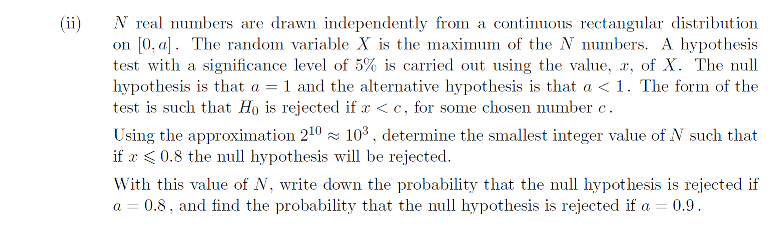
Hypothesis testing the continuous rectangular distribution (STEP Question 13 Paper I 2004)

What do you know about probabilities when draws are independent? If you want the maximum of the numbers to be less than 0.8, what can you say about each of the numbers themselves?

What is the probability now that \( x \) is less than \(0.8\)? How can use the approximation in this to rearrange for \(N\)?
Well done if you've managed to complete any of these questions! If not, don't worry, mastering any topic in STEP can require a lot of practice. Fortunately, for Statistics questions in particular there is an abundance available and they're very easy to find: open any STEP past paper and turn to Section C and you should find something to challenge yourself with.

