Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Positive Differences



- Problem
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources
Amélie from St Nicholas CE Primary School in England sent in this completed diagram:
Anna from Crestwood Community School sent this completed diagram:
Jean from Holy Child Killiney, Year 5 Wellington College Shanghai in China, Elsie from Pates' Grammar School, Miraya from Heckmondwike Grammar School, Noah, Tom, Toby and Evan from the King's School Grantham and Rohan from Wilson's School, all in the UK, Kyra, Ollie, Eric, Peter, Jada, Lydia, Jack and Sydni from Greenville Classical Academy in the USA, Emma from Caxton College in Spain and Ramsha from Doha College in Qatar explained why $6$ must be in the bottom row. Noah, Tom, Toby and Evan wrote:
No pair of numbers between 1-6 has a difference of 6.
Ci Hui Minh Goc from Kelvin Grove State College (Brisbane) in Australia illustrated this idea with a picture:
Jean, Ci Hui Minh Ngoc, Emma, Elsie, Ramsha, Noah, Tom, Toby and Evan, Kyra, Ollie, Eric, Peter, Jada, Lydia, Jack, Sydni, Rohan, Miraya and Year 5 explained why $5$ cannot go at the top. This is Ramsha's work:
Let’s say that we did put 5 at the top, the only two numbers within the 1-6 range we can use are 1 and 6. However, we have already addressed the problem with having 6 anywhere but the bottom which is why we can’t have 5 at the top.
Jean, Ci Hui Minh Ngoc, Emma, Kyra, Ollie, Eric, Peter, Jada, Lydia, Jack, Sydni, Elsie, Ramsha, Noah, Tom, Toby and Evan, Rohan, Miraya and Year 5 explained why $4$ cannot go at the top. This is Miraya's work:
If 4 was placed on the top then there would be two possible combinations of numbers to go on the second row. It could be either 2&6 or 1&5.
2&6 would not be possible because 6 has to be on the bottom row since there are not any numbers between the range of 1 and 6 that can have a difference of 6.
1&5 would also not be possible because the numbers below would have to use 1 and that is not possible because you can only use each number once.
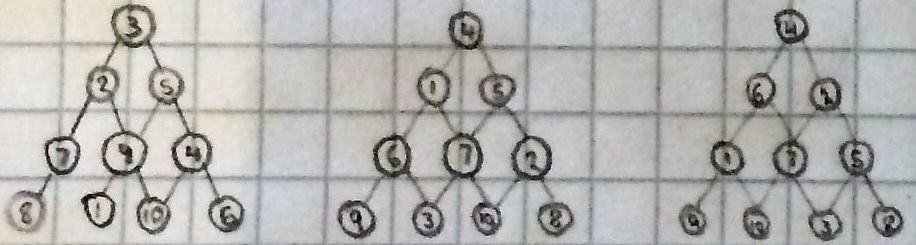
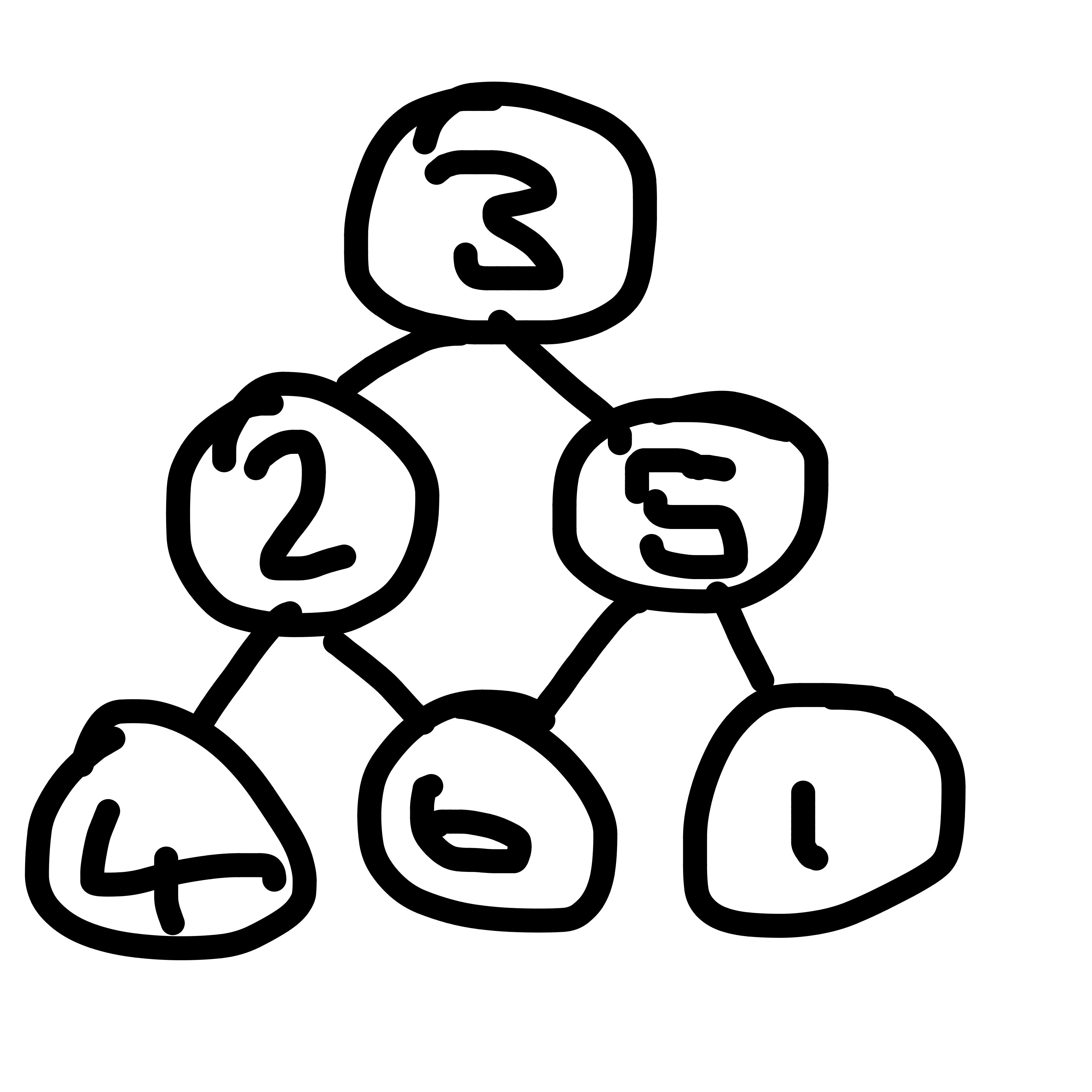
Samuel and Brayden from Olympus International Academy in the United States, Miraya, Ramsha and Year 5 each found three possible solutions and Leo from Olympus International Academy, Noah, Tom, Toby and Evan, Elsie, Kyra, Ollie, Eric, Peter, Jada, Lydia, Jack, Sydni and Rohan found four. Rohan and Kyra, Ollie, Eric, Peter, Jada, Lydia, Jack, Sydni and Emma used a systematic method to show that those are all of the possible solutions. This is Kyra, Ollie, Eric, Peter, Jada, Lydia, Jack and Sydni's work:
We say there are only four solutions.
1
3 - 4
5 - 2 - 6
This is the only solution with 1 in the first row. We know this because we tested all the possibilities for the second row.
2 - 1 cannot be because we already used 1.
3 - 2 doesn't work because 4, 5, and 6 cannot be in the third row.
5 - 4 doesn't work because you would need 6 - 1 in the third row but we have already used 1.
6 - 5 doesn't work because 6 must be in the last row.
2
5 - 3
6 - 1 - 4
This is the only solution with 2 in the top row.
3 - 1 cannot be in the second row because that would leave 4, 5, and 6 in the third row.
4 - 2 doesn't work because we have already used 2.
6 - 4 doesn't work because 6 must be in the third row.
3
4 - 1
2 - 6 - 5
3
5 - 2
1 - 6 - 4
These are the only two solutions with 3 in the top.
The only other possible pair to give a difference of 3 is 6 - 3 which doesn't work in the second because we have already used 3 and 6 must be in the third row.
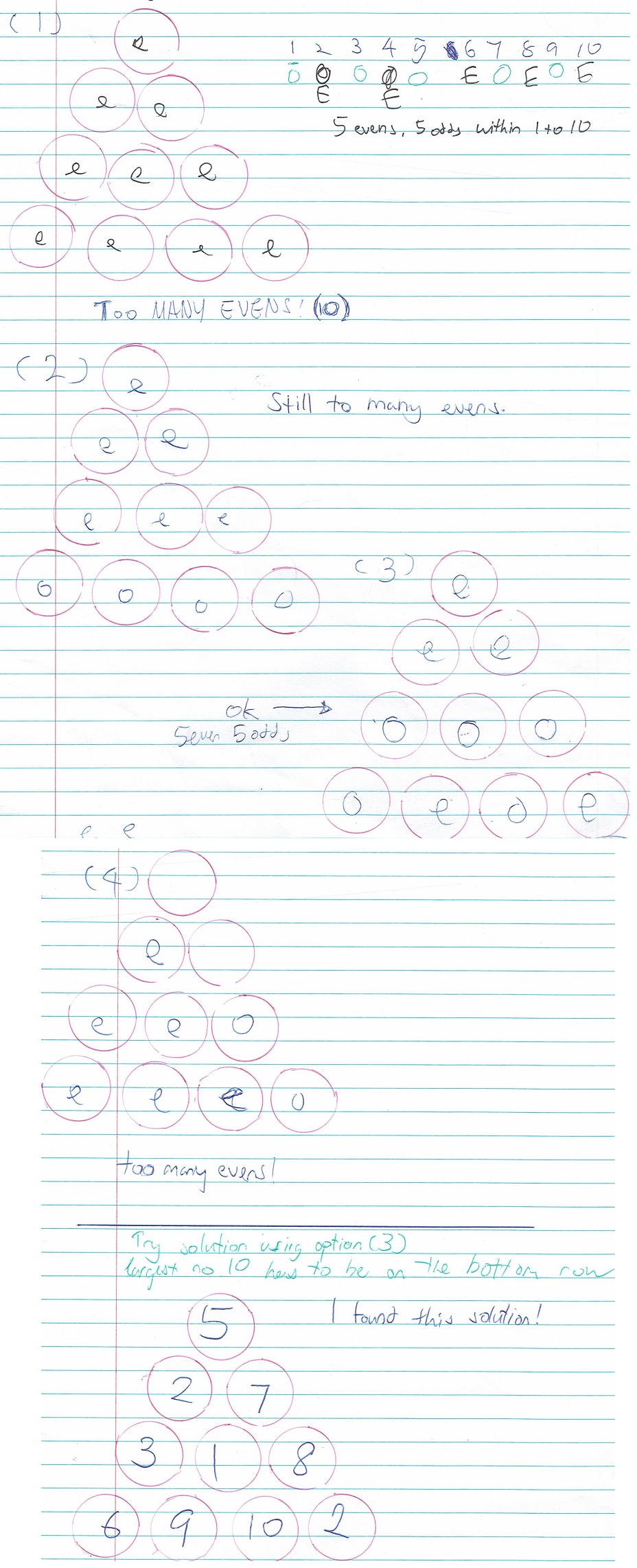
Ci Hui Minh Ngoc thought about where the odd and even numbers could go:
Could this help you convince yourself that we've found all the possible solutions?
For the extension, Rohan found a solution using the numbers 1-10:
Elsie described some rules about where the 10 and the 9 could go:
10 cannot be in the top row because there are no two numbers (in this instance) that have a difference of 10. The only place 10 can go is in the top row.
9 cannot be in the top row because (in this instance) there is only 1 pair of numbers that have a difference of 9: 10 and 1. As 10 can only go in the bottom row, 9 can't go in the top row.
Elsie found three solutions using the numbers 1 to 10 (click on the image to see a larger version):
Year 5 from Wellington College found a solution which was the same as Elsie's middle solution.
Kyra, Ollie, Eric, Peter, Jada, Lydia, Jack and Sydni wrote some more rules:
8 must be in the 4th row.
9 and 1 cannot be side by side in the third row.
1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 10 cannot be in the top row.
Can you explain why their rules are true?
They found four solutions using the numbers 1 to 10, which are the same as Rohan's solution and Elsie's three solutions.
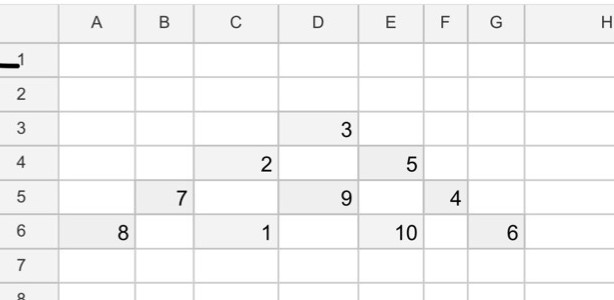
Emma found solutions using a spreadsheet:
I did an excel spreadsheet putting the formula D3=ABS(C4-E4) as an example. And then I started playing with the numbers at the bottom to get the solution in the photo.
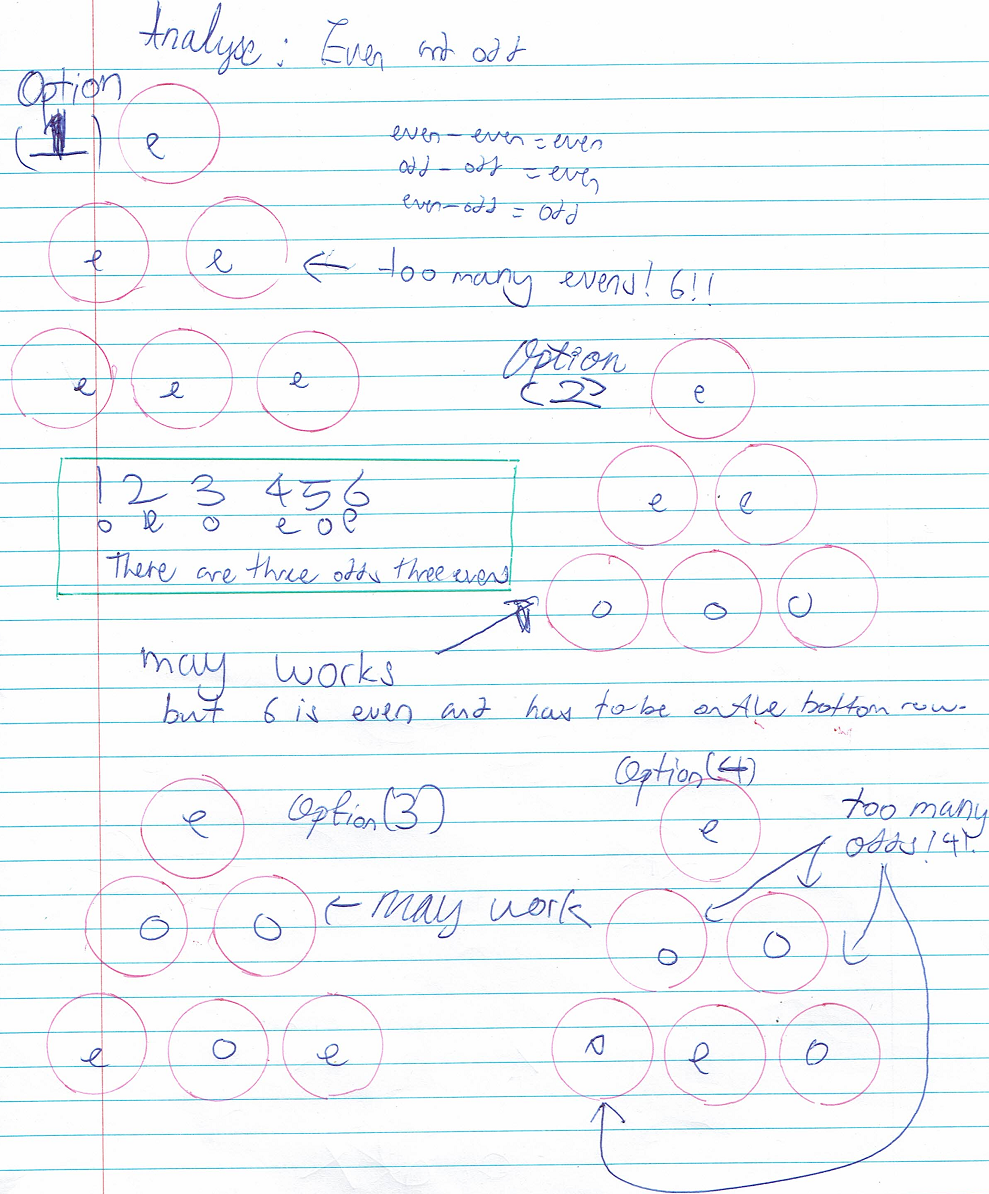
Ci Hui Minh Ngoc thought about where the odd and even numbers could go, and used this to find a solution: