Skip over navigation
Answer: 24 miles per hour
Working out the distance using numbers
The difference between 3 minutes late and 3 minutes early is 6 minutes
Try out different distances to get a difference of 6 minutes
That means Ms Fanthorpe wants to travel 6 miles in 15 minutes, which means she needs to travel at 24 miles per hour.
Using a distance-time graph
The two lines on this distance-time graph represent Ms Fanthorpe travelling at 20 miles per hour (blue) and 30 miles per hour (orange).
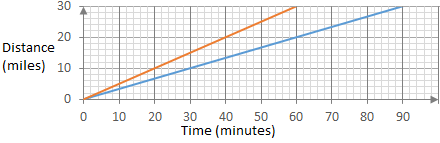
Method 1: At what distance is the difference 6 minutes?
The difference between 3 minutes late and 3 minutes early is 6 minutes.
This happens at 6 miles, because there the time on the blue line is 18 minutes and the time on the orange line is 12 minutes.
Ms Fanthorpe wants to travel 6 miles in 15 minutes, which means she needs to travel at 24 miles per hour.
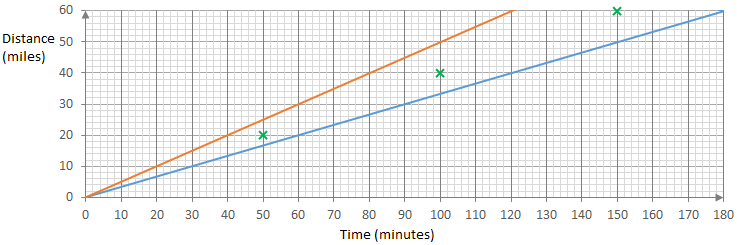
Method 2: Finding journeys where the arrival time is half-way between the arrival times at 20 and 30 miles per hour
For example, travelling 60 miles takes 120 minutes at 30 miles per hour or 180 minutes at 20 miles per hour, so half-way between these times is 150 minutes.
Travelling 40 miles takes 80 or 120 minues, so half-way between these times is 100 minutes. Travelling 20 miles takes 40 or 60 minutes, so half-way between these times is 50 minutes. These are shown on the graph below.
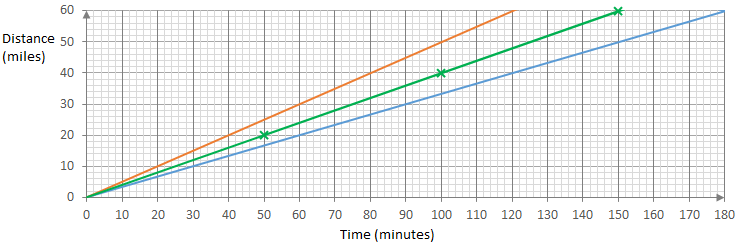
Joining these green points up gives a straight line.
The green line represents a journey at a constant speed of 24 miles per hour.
So Ms Fanthorpe should drive at an average speed of 24 miles per hour.
Using Algebra
Aim to arrive at work $t$ minutes after 8:30.
At $20$ miles per hour it takes $t+3$ minutes
At $30$ miles per hour it takes $t-3$ minutes
The distance = her average speed $\times$ journey time.
$20$ miles per hour = $\frac{1}{3}$ miles per minute
$30$ miles per hour = $\frac{1}{2}$ miles per minute
This means the distance to work = $\frac{1}{3}\times(t+3)$ (travelling at $20$ mph)
= $\frac{1}{2}\times(t-3)$ (travelling at $30$ mph)
= $s\times t$ (travelling at $s$ mph to arrive on time)
$\frac{1}{3}(t+3)=\frac{1}{2}(t-3)\Rightarrow t=15$
distance to work = $\frac{1}{3}\times(15 + 3) = 6$, miles
$s=6\div15=\frac{2}{5}$ miles per minute, which is the same as $24$ miles per hour.
It is also possible to find the speed without finding the distance. This means that the units don't matter, so we can use $20(t+3)$ and $30(t-3)$ as expressions for the distance.Then $20(t+3)=30(t-3)$ gives $t=15$, and substituting into $20(t+3)=st$ gives $20\times18=st$, so $s=24$.

Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Late for Work
Age 14 to 16
ShortChallenge Level 





- Problem
- Solutions
Answer: 24 miles per hour
Working out the distance using numbers
The difference between 3 minutes late and 3 minutes early is 6 minutes
Try out different distances to get a difference of 6 minutes
| distance | time at 20 mph | time at 30 mph | difference | comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 miles | 3 hours | 2 hours | 1 hour = 60 min | too far |
| 10miles | 30 minutes | 20 minutes | 10 minutes | too far |
| 5 miles | 15 minutes | 10 minutes | 5 minutes | too close |
| 6 miles | 18 minutes | 12 minutes | 6 minutes | correct distance |
That means Ms Fanthorpe wants to travel 6 miles in 15 minutes, which means she needs to travel at 24 miles per hour.
Using a distance-time graph
The two lines on this distance-time graph represent Ms Fanthorpe travelling at 20 miles per hour (blue) and 30 miles per hour (orange).

Method 1: At what distance is the difference 6 minutes?
The difference between 3 minutes late and 3 minutes early is 6 minutes.
This happens at 6 miles, because there the time on the blue line is 18 minutes and the time on the orange line is 12 minutes.
Ms Fanthorpe wants to travel 6 miles in 15 minutes, which means she needs to travel at 24 miles per hour.
Method 2: Finding journeys where the arrival time is half-way between the arrival times at 20 and 30 miles per hour
For example, travelling 60 miles takes 120 minutes at 30 miles per hour or 180 minutes at 20 miles per hour, so half-way between these times is 150 minutes.
Travelling 40 miles takes 80 or 120 minues, so half-way between these times is 100 minutes. Travelling 20 miles takes 40 or 60 minutes, so half-way between these times is 50 minutes. These are shown on the graph below.

Joining these green points up gives a straight line.
The green line represents a journey at a constant speed of 24 miles per hour.
So Ms Fanthorpe should drive at an average speed of 24 miles per hour.

Using Algebra
Aim to arrive at work $t$ minutes after 8:30.
At $20$ miles per hour it takes $t+3$ minutes
At $30$ miles per hour it takes $t-3$ minutes
The distance = her average speed $\times$ journey time.
$20$ miles per hour = $\frac{1}{3}$ miles per minute
$30$ miles per hour = $\frac{1}{2}$ miles per minute
This means the distance to work = $\frac{1}{3}\times(t+3)$ (travelling at $20$ mph)
= $\frac{1}{2}\times(t-3)$ (travelling at $30$ mph)
= $s\times t$ (travelling at $s$ mph to arrive on time)
$\frac{1}{3}(t+3)=\frac{1}{2}(t-3)\Rightarrow t=15$
distance to work = $\frac{1}{3}\times(15 + 3) = 6$, miles
$s=6\div15=\frac{2}{5}$ miles per minute, which is the same as $24$ miles per hour.
It is also possible to find the speed without finding the distance. This means that the units don't matter, so we can use $20(t+3)$ and $30(t-3)$ as expressions for the distance.Then $20(t+3)=30(t-3)$ gives $t=15$, and substituting into $20(t+3)=st$ gives $20\times18=st$, so $s=24$.
You can find more short problems, arranged by curriculum topic, in our short problems collection.
You may also like
Ladder and Cube
A 1 metre cube has one face on the ground and one face against a wall. A 4 metre ladder leans against the wall and just touches the cube. How high is the top of the ladder above the ground?
Bendy Quad
Four rods are hinged at their ends to form a convex quadrilateral. Investigate the different shapes that the quadrilateral can take. Be patient this problem may be slow to load.

