Skip over navigation
Answer: 7.5 m/s
Using the speed-distance-time relationship
2 minutes = 120 seconds at 6 metres/second, Dolly swims 120$\times$6 = 720 metres.
Against 2 m/s current: 6 m/s
No current: 8 m/s
With 2 m/s current: 10 m/s
Travelling 720 metres at 10 m/s will take 72 seconds.
Total distance: 720 + 720 = 1440 metres
Total time: 120 + 72 = 192 seconds.
Average speed of 1440 $\div$ 192 = 360 $\div$ 48 = 45 $\div$ 6 = 7.5 m/s.
Swimming 30 metres each way
Against 2 m/s current: 6 m/s
No current: 8 m/s
With 2 m/s current: 10 m/s
30 metres is a multiple of 6 metres and of 10 metres
30 = 6$\times$5 so 30 metres takes 5 seconds on the way
30 = 3$\times$10 so 30 metres takes 3 seconds on the way back
Total 60 metres takes 8 seconds so average speed is 60$\div$8 = 7.5
Using a graph
Green: upstream, 6 m/s
Red: downstream, 10 m/s
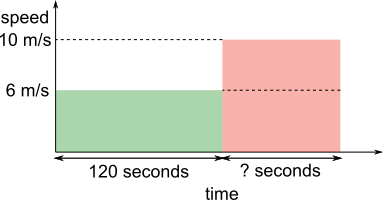
On a speed-time graph, the area represents the distance travelled
Green area + Red area = total distance travelled.
On the two graphs below, the difference between the heights is split into two parts.
The yellow rectangle is moved and reshaped into the first 120 seconds without changing the area and the heights are the same. This represents finding the average speed, because now the same distance is travelled in the same amount of time, but without changing speed.
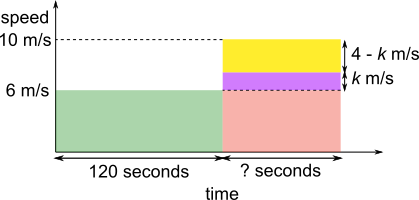
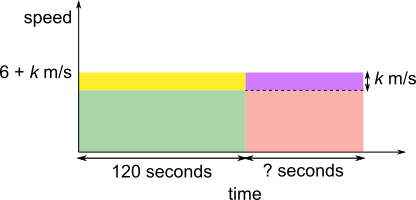
The two yellow rectangles are equal in area, and have bases 120 and ?.
The red and green rectangles in the first diagram are also equal in area with bases 120 and ?.
So the ratio between the heights of the yellow rectangles must be the same as the ratio between the heights of the green and red rectangles.
So $k:4-k$ is equivalent to $6:10$
$k+4-k=4$ and $6+10=16$, so since $16$ is $4$ times bigger than $4$, everything in the ratio $6:10$ is $4$ times bigger than everything in the ratio $k:4-k$.
So $k=6\div4=1.5$, and so the average speed is $6+1.5=7.5$ m/s.

Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Dolly Dolphin
Age 14 to 16
ShortChallenge Level 





- Problem
- Solutions
Answer: 7.5 m/s
Using the speed-distance-time relationship
average speed = total distance travelled $\div$ total time taken
2 minutes = 120 seconds at 6 metres/second, Dolly swims 120$\times$6 = 720 metres.
Against 2 m/s current: 6 m/s
No current: 8 m/s
With 2 m/s current: 10 m/s
Travelling 720 metres at 10 m/s will take 72 seconds.
Total distance: 720 + 720 = 1440 metres
Total time: 120 + 72 = 192 seconds.
Average speed of 1440 $\div$ 192 = 360 $\div$ 48 = 45 $\div$ 6 = 7.5 m/s.
Swimming 30 metres each way
Against 2 m/s current: 6 m/s
No current: 8 m/s
With 2 m/s current: 10 m/s
30 metres is a multiple of 6 metres and of 10 metres
30 = 6$\times$5 so 30 metres takes 5 seconds on the way
30 = 3$\times$10 so 30 metres takes 3 seconds on the way back
Total 60 metres takes 8 seconds so average speed is 60$\div$8 = 7.5
Using a graph
Green: upstream, 6 m/s
Red: downstream, 10 m/s

On a speed-time graph, the area represents the distance travelled
Green area + Red area = total distance travelled.
On the two graphs below, the difference between the heights is split into two parts.
The yellow rectangle is moved and reshaped into the first 120 seconds without changing the area and the heights are the same. This represents finding the average speed, because now the same distance is travelled in the same amount of time, but without changing speed.


The two yellow rectangles are equal in area, and have bases 120 and ?.
The red and green rectangles in the first diagram are also equal in area with bases 120 and ?.
So the ratio between the heights of the yellow rectangles must be the same as the ratio between the heights of the green and red rectangles.
So $k:4-k$ is equivalent to $6:10$
$k+4-k=4$ and $6+10=16$, so since $16$ is $4$ times bigger than $4$, everything in the ratio $6:10$ is $4$ times bigger than everything in the ratio $k:4-k$.
So $k=6\div4=1.5$, and so the average speed is $6+1.5=7.5$ m/s.
You can find more short problems, arranged by curriculum topic, in our short problems collection.
You may also like

Percentage Unchanged
If the base of a rectangle is increased by 10% and the area is unchanged, by what percentage is the width decreased by ?

