Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
A Complex Mistake?
This article is part of our Adventures with Complex Numbers collection
At the end of the first century AD, the Greek mathematician Heron of Alexandria missed the chance to explore a brand new area of mathematics. He was interested in frustums - truncated pyramids with a square base and top, joined by straight sloping sides. In his book Stereometria he asked the question: If the length of the sides of the square base is a, the length of the sides of the square top is b, and the length of the sloping edges running from top to bottom is c, how high is your frustum?
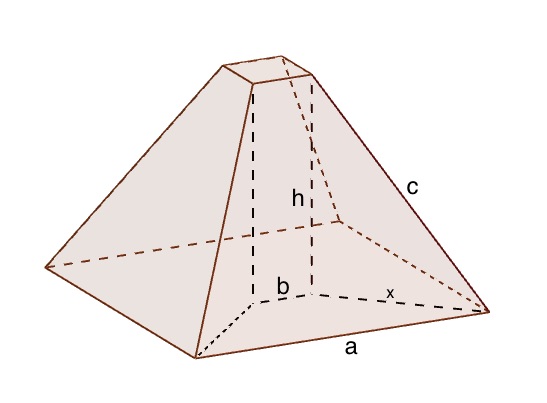
This frustum is drawn with the values a=10, b=2, c=9 and h=7.
He came up with this tidy formula (you can see how here) for calculating the height, $h$, of a frustum: $$ h = \sqrt{c^2 - \frac{(a-b)^2}{2}}. $$ He demonstrated his formula first with the example of a frustum with a base with sides of length $a=10$, top with sides of length $b=2$ and sloped sides of length $c=9$. He could easily calculate that the height, $h$, of such a shape was 7, using his formula: $$ h = \sqrt{c^2 - \frac{(a-b)^2}{2}} = \sqrt{81 - \frac{64}{2}} = \sqrt{49} = 7. $$
Heron then tried this approach for a different example, with a base of side length $a=28$, top of side length $b=4$ and sloped edge of length $c=15$. This time his formula gives the height as: $$ h = \sqrt{c^2 - \frac{(a-b)^2}{2}} = \sqrt{225 - 288} = \sqrt{-63}. $$
Heron had managed to come up with an impossible example: no frustum with these measurements could exist. But he had also come up with the first recorded example we have of a calculation involving the square root of a negative number, a complex number. The answer was recorded in his book, however, as $\sqrt{63}$. We don't know if he deliberately ignored the strange result or simply
made a mistake and didn't notice. But he definitely missed his complex opportunity.
You can explore complex numbers for yourself in Open the Door, and discover more about the many applications of complex numbers with this collection of articles on Plus.

