Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Digit Addition



- Problem
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources
We had a small number of submissions for this task and here are some for you to consider.
Emma and Ruby from Tolkien Class, Yewdale Primary School wrote:
We agree with Jonas but we have a different way to explain it. He said that adding 9 is the same as adding 10 and subtracting 1.
Our working out:
1 + 9 = 10 1 + 0 = 1
2 + 9 = 11 1 + 1 = 2
3 + 9 = 12 1 + 2 = 3
4 + 9 = 13 1 + 3 = 4
5 + 9 = 14 1 + 4 = 5
6 + 9 = 15 1 + 5 = 6
7 + 9 = 16 1 + 6 = 7
8 + 9 = 17 1 + 7 = 8
9 + 9 = 18 1 + 8 = 9
So we conclude that every time you add 9 to a number from 1 to 9 and then add your answers digits together, you will always get the same number you started with. If you wrote 1 to 9 you will get the same order back.
Here's proof that you can't go over 10:
23 + 9 = 32 3 + 2 = 5
A teacher at Olga Primary School wrote about her class' work:
We started off by doing the 'number trick'. The children then practised this in their books to make sure it happened every time.
After we'd established that this rule was always correct i.e. you always end up with the number you started with, I asked the children to discuss in small groups why they thought this was the case. I listened to different children and this is what they said:
Mutahara: "I did it 1, 2, 3, 4 in order, and the answers went 10, 11, 12, 13... in order"
Yusuf said: "9 is one less than 10, and 1 is one less than 2" (We were looking at 2 + 9 as an example.)
"I notice that the 1st ones number is bigger than the 2nd ones number. It's 1 bigger, and 9 is one smaller than ten."
"You're just adding 10s to the number and when you partition you just ignore the tens." I asked him what he meant by 'ignore' and he wasn't able to explain.
Francis said: "If you add ten it will be ten more so one less must be the same... Adding 10 is just adding a 1 on the front (to the tens column) and if you then -1 it will = one less. We're adding 9, which is one less than ten."
We then agreed as a class that adding 9 was the same as +10 and -1, and tested this hypothesis using different numbers. Once we'd all agreed this was true, we resumed our small group discussions:
Ryu said: "Because there's a one in the tens, if you break down the ones column, and pretend there's not such thing as a tens column, you're really just adding one."
We re-convened and collated what we knew. I asked the children to think about why we always end up in the tens column. In his explanation, Amaan said "9 is next to ten", and used the word 'inverse'. I asked him to elaborate. "Plus is the opposite of minus," he said.
Milo responded to this excitedly with the equation '1+1-1=1'.
We explored this concept with different numbers, e.g. 6+1-1=6, and decided that since we were taking a number, +10 then -1, then recombining the digits, that was essentially the same as +1-1, therefore we always ended up with the number we started with.
I (the teacher) loved working through this with the children and listening to their explanations.
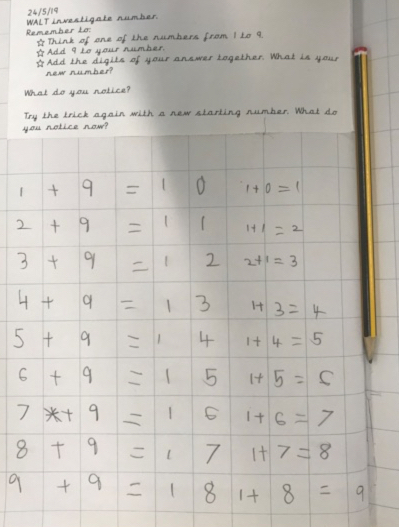
Thank you to this teacher for taking the time to send us this description of the thinking unfolding in the classroom. It is wonderful to read about the children's journey as they tackled this task.
Issy and Neve from St. Andrews School C. of E. Primary School Halstead wrote:
When you pick a number between 1 and 10, for an example you could choose 2 and then you would add 9 and then add them together it will equal 11 and then you would add 1 and 1 together you will get your original number.
Here are the examples:
1 + 9 = 10 1 + 0 = 1
2 + 9 = 11 1 + 1 = 2
3 + 9 = 12 1 + 2 = 3
4 + 9 = 13 1 + 3 = 4
5 + 9 = 14 1 + 4 = 5
6 + 9 = 15 1 + 5 = 6
7 + 9 = 16 1 + 6 = 7
8 + 9 = 17 1 + 7 = 8
9 + 9 = 18 1 + 8 = 9
This works because whenever you add by 9 it is always one less than the number you were adding to so if you were adding something like 6 to 9 it would equal 15 and the 5 is 1 less than the 6 and if you add 1 it would go back to the original number [6].
Izzy and Neve also explored using numbers 1-10 and some higher numbers to multiply by 9, rather than adding 9, for example:
1 x 9 = 9 and 0 + 9 = 9
2 x 9 = 18 and 1 + 8 = 9
3 x 9 = 27 and 2 + 7 = 9
4 x 9 = 36 and 3 +6 = 9
5 x 9 = 45 and 4 + 5 = 9
6 x 9 = 54 and 5 + 4 = 9
7 x 9 = 63 and 6 + 3 = 9
8 x 9 = 72 and 7 + 2 = 9
9 x 9 = 81 and 8 + 1 = 9
9 x 10 = 90 and 9 + 0 = 9
9 x 12 = 108 and 1 + 0 + 8 = 9
This time, when the digits of the answer are added, something different happens... You may wish to explore this further!
Thank you to everyone for your well explained solutions.
Related Collections
You may also like
Writing Digits
Lee was writing all the counting numbers from 1 to 20. She stopped for a rest after writing seventeen digits. What was the last number she wrote?
Six Is the Sum
What do the digits in the number fifteen add up to? How many other numbers have digits with the same total but no zeros?

