Skip over navigation
A number of correct answers to the above were received which included:

Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Snookered
Age 14 to 18
Challenge Level 





- Problem
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources
A number of correct answers to the above were received which included:
- The brown ball cannot be potted off just one cushion.
-
Playing off two cushions the brown ball can be potted off two cushions in three ways. The three points that must be aimed at have coordinates (4.2, 6) (9, 3.75) and (0, 0.75)
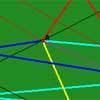
The diagram shows the snooker table and 15 copies of the table. The path of the ball after bouncing off a wall (reflection) is shown by a straight line in the adjacent copy of the table.

The snooker table is bounded by the lines $x=0$, $x=9$, $y=0$ and $y=6$.
The white ball is at W(3, 3), the brown (target ball T) is at (9, 6), the pink is at (7, 3), the black is at (7, 5) and the blue is at (1, 4).
With no other balls in the way, travelling initially in the direction WA or WB, the white ball would hit the target having bounced off one wall.
With no other balls in the way, travelling initially in the direction WC, WD or WE, the white ball would hit the target having bounced off two walls.
With no other balls in the way, travelling initially in the direction WF or WH, the white ball would hit the target having bounced off three walls and in the direction WG it would bounce off 4 walls.
This pattern can of course be extended in all directions to show bouncing off 4 or more walls.
OA has gradient ${-3\over 2}$ and goes through the point (7, -3) so the pink ball at (7, 3) would be in the path of the white ball.
OB has gradient ${-1\over 4}$ and goes through the point (-1, 4) so the blue ball at (1, 4) would be in the path of the white ball.
OC has gradient ${5\over 2}$ and hits the first wall at (4.2, 6) bouncing off two walls parallel to the x axis before hitting the brown ball. None of the other balls is in its path.
OD has gradient ${1\over 8}$ and hits the first wall at (9, 3.75) bouncing off two walls parallel to the y axis before hitting the brown ball.
OE has gradient ${3\over 4}$ and hits the first wall at (0, 0.75) bouncing off two walls, one parallel to the y axis and one to the x axis, before hitting the brown ball.
OF has gradient ${-5\over 4}$ and hits the first wall at (0.6, 6) bouncing off three walls before hitting the brown ball.
OG has gradient ${5\over 8}$ and hits the first wall at (7.8, 6) bouncing off four walls before hitting the brown ball.
OH has gradient ${5\over 8}$ and hits the first wall at (9, 0.75) bouncing off three walls before hitting the brown ball.
You may also like
Cushion Ball
The shortest path between any two points on a snooker table is the straight line between them but what if the ball must bounce off one wall, or 2 walls, or 3 walls?
Retracircles
Four circles all touch each other and a circumscribing circle. Find the ratios of the radii and prove that joining 3 centres gives a 3-4-5 triangle.
A Problem of Time
Consider a watch face which has identical hands and identical marks for the hours. It is opposite to a mirror. When is the time as read direct and in the mirror exactly the same between 6 and 7?

