Skip over navigation

Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Right or Left?
Age 7 to 11
Challenge Level 





- Problem
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources
Right or Left?
You may know that opposite faces of a dice add up to $7$, but did you know that there are two different types of dice?
Here are two dice, a right-handed one and a left-handed one:
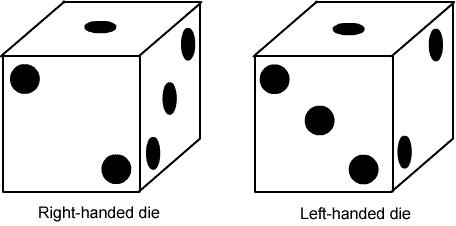
Decide whether the dice below are right-handed or left-handed:
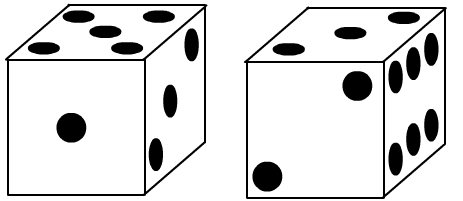
Now try these - they are more difficult.
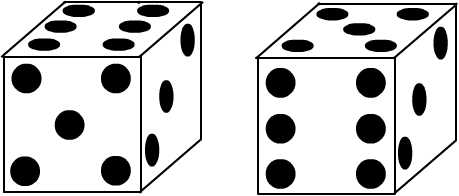
This problem is taken from the book "Mathematical Activities from Poland" published by ATM.
Why do this problem?
This problem encourages children to explore dice in more detail. Even though they may use them frequently, they may not have thought about a dice's properties before. They will be challenged to visualise the dice but making nets of cubes might also be helpful.
Key questions
What do opposite sides of the dice add to?
Can you imagine turning the dice so that you can compare it with the pictures of the right-handed and left-handed dice more easily?
If the $1$ is at the top of the dice and the $2$ facing you, where is the $3$ on the right-handed dice/left-handed dice?
Have a look at the dice in our classroom, are they left-handed or right-handed?
Possible support
If learners are having trouble with the visualisation and you don't have left-handed and right-handed dice, they could stick spots onto cubes to help. Alternatively, print off this sheet which has a net of a right-hand dice on the first page and
a net of a left-handed dice on the second.
You may also like
Little Boxes
How many different cuboids can you make when you use four CDs or DVDs? How about using five, then six?

