Skip over navigation


Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Mesh
Age 16 to 18
Challenge Level 





- Problem
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources
Thomas Lauffenberger, who did not give his school or country, and
Andrei Lazanu from School No. 205, Bucharest, Romania sent in
correct solutions to this problem.
Here is Thomas's solution:
For the balloon to escape its mortal coil (er, cage), it must shrink to match the radius of a hole through one of the octants of the spherical cage. Figuring out this hole requires us to consider two types of equilateral triangles, one in the plane and one with 3 right angles layered onto the cage's surface.
With the triangle in the plane, we can inscribe a circle tangent to the midpoints of the sides; extrapolate this idea to the arcs making the "triangle" of the cage octant. The inscribed circle (with respect to the arcs) is now a circumscribed circle with respect to the triangle formed by the midpoints of the arcs. Since we're working with a unit sphere balloon, if we draw the 3-D axes and sketch in the octant (or use a globe and pick the one containing Europe), the three points would be at $45^o$N $0^o$E/W ($7^o$ south of London), $45^o$N $90^o$E(guessing that's Russia somewhere), and $0^o$N $45^o$E (your guess is as good as mine), or, on a unit globe, $(\sqrt 2/2, 0, \sqrt 2/2),\ (0, \sqrt 2/2,\sqrt 2/2)$, and $(\sqrt 2/2, \sqrt 2/2, 0)$. Applying the distance formula to these points, each one is 1 unit from the other.
Being an equilateral triangle, the center of the outer circle and the triangle are the same, and, using the property of the orthocenter, we find the length from a vertex to the center to be $1/\sqrt 3$ units. This is the radius needed for the balloon to escape.
This is Andrei's solution:
First I observed that the eight parts in which the sphere was divided are equal. So, it is sufficient to consider one part of the frame.
To find the sphere that passes through this frame, I have to find the greatest circle of the sphere. I observe that I have to find the radius of the inscribed circle in the curvilinear triangle ABC, with edges quarters of great circles of the original sphere.
Due to the symmetry, this triangle has all sides congruent, so the inscribed circle will touch its sides in the middles of the arcs. Let M, N and P be the middles of arcs AB, BC and AC respectively. All I have to do is to find the radius of the circumscribed circle of triangle MNP (with normal sides).
Now, I find the sides of triangle MNP.
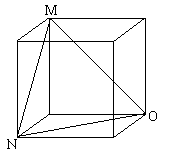
As M is the middle of arc AB, OM is the angle bisector of AOB. So is NO for angle BOC. Now I want to find the angle between OM and ON. \par In the cube below, OM and ON are in the same positions as OM and ON in the sphere. OM and ON are congruent, but they are also congruent with MN, so that triangle MNO is equilateral, and the angle between OM and ON has a measure of $60^o$.
 So, in the sphere, triangle OMN is equilateral, with side of length
R. Consequently, triangle MNP is also equilateral, and has the
length of the side equal with the radius of the original sphere.
The radius of the circumscribed circle of triangle MNP is $R\sqrt3
/3$ where $R$ is the radius of the original sphere. As I said
before, this is also the radius of the sphere that passes through
the hole.
So, in the sphere, triangle OMN is equilateral, with side of length
R. Consequently, triangle MNP is also equilateral, and has the
length of the side equal with the radius of the original sphere.
The radius of the circumscribed circle of triangle MNP is $R\sqrt3
/3$ where $R$ is the radius of the original sphere. As I said
before, this is also the radius of the sphere that passes through
the hole.
Here is Thomas's solution:
For the balloon to escape its mortal coil (er, cage), it must shrink to match the radius of a hole through one of the octants of the spherical cage. Figuring out this hole requires us to consider two types of equilateral triangles, one in the plane and one with 3 right angles layered onto the cage's surface.
With the triangle in the plane, we can inscribe a circle tangent to the midpoints of the sides; extrapolate this idea to the arcs making the "triangle" of the cage octant. The inscribed circle (with respect to the arcs) is now a circumscribed circle with respect to the triangle formed by the midpoints of the arcs. Since we're working with a unit sphere balloon, if we draw the 3-D axes and sketch in the octant (or use a globe and pick the one containing Europe), the three points would be at $45^o$N $0^o$E/W ($7^o$ south of London), $45^o$N $90^o$E(guessing that's Russia somewhere), and $0^o$N $45^o$E (your guess is as good as mine), or, on a unit globe, $(\sqrt 2/2, 0, \sqrt 2/2),\ (0, \sqrt 2/2,\sqrt 2/2)$, and $(\sqrt 2/2, \sqrt 2/2, 0)$. Applying the distance formula to these points, each one is 1 unit from the other.
Being an equilateral triangle, the center of the outer circle and the triangle are the same, and, using the property of the orthocenter, we find the length from a vertex to the center to be $1/\sqrt 3$ units. This is the radius needed for the balloon to escape.
This is Andrei's solution:
First I observed that the eight parts in which the sphere was divided are equal. So, it is sufficient to consider one part of the frame.
To find the sphere that passes through this frame, I have to find the greatest circle of the sphere. I observe that I have to find the radius of the inscribed circle in the curvilinear triangle ABC, with edges quarters of great circles of the original sphere.
Due to the symmetry, this triangle has all sides congruent, so the inscribed circle will touch its sides in the middles of the arcs. Let M, N and P be the middles of arcs AB, BC and AC respectively. All I have to do is to find the radius of the circumscribed circle of triangle MNP (with normal sides).
Now, I find the sides of triangle MNP.
As M is the middle of arc AB, OM is the angle bisector of AOB. So is NO for angle BOC. Now I want to find the angle between OM and ON. \par In the cube below, OM and ON are in the same positions as OM and ON in the sphere. OM and ON are congruent, but they are also congruent with MN, so that triangle MNO is equilateral, and the angle between OM and ON has a measure of $60^o$.

You may also like
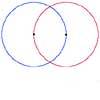
2D-3D
Two circles of equal size intersect and the centre of each circle is on the circumference of the other. What is the area of the intersection? Now imagine that the diagram represents two spheres of equal volume with the centre of each sphere on the surface of the other. What is the volume of intersection?
The Dodecahedron Explained
What is the shortest distance through the middle of a dodecahedron between the centres of two opposite faces?
When the Angles of a Triangle Don't Add up to 180 Degrees
This article outlines the underlying axioms of spherical geometry giving a simple proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle on the surface of a unit sphere is equal to pi plus the area of the triangle.

