Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Published 2002 Revised 2011
Multiplication Series: Number Arrays
Using Arrays to Explore Numbers
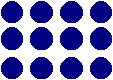
Arrays are useful models for multiplication which can be used in a variety of ways, ranging from highly structured lessons to games and open investigations. An array is formed by arranging a set of objects into rows and columns. Each column must contain the same number of objects as the other columns, and each row must have the same number as the other rows.
The following array, consisting of four columns and three rows, could be used to represent the number sentence 3 x 4 = 12.
Building Number Facts

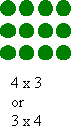
Odds and Evens
The concepts of odd and even numbers are somewhat bewildering to many young children, so having a method to model numbers that clearly shows the difference between odds and evens is crucial. Even numbers can be made into two-row arrays, but odd numbers cannot - there being always one item left over. The making of two rows highlights the fact that even numbers are always divisible by two.

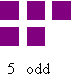

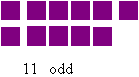
Exploring factors
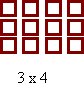
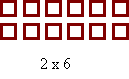
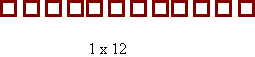
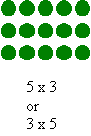
Exploring factors in this way will lead to the discovery that some numbers can be made into more than one array (that is; composite numbers), and some numbers can only be represented by one-row arrays (that is; prime numbers).


Another investigation of factors using arrays is the search for numbers that can form square arrays; namely, the square numbers .


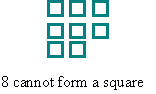
Grid paper can be useful for recording the findings of such investigations. Problems such as those below can provide consolidation of the discoveries made by young children.


