Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
The Thousands Game



- Problem
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources
The Thousands Game
The Thousands Game printable sheet
Class 3 were playing a game. There were ten cards with the digits $0$ to $9$ on them.

These cards were put into a bag and players took out four cards and made a number out of them. At first they made the highest number they could. Sinita took out
 |
and made |  |
Then they made the lowest number they could. Jamie took out
 |
and made |  |
"You can't put zero at the beginning of a number," objected Paul. The class discussed this and decided that Jamie had made four hundred and fifty-seven.
Next they played to make the highest even number. Jill took out
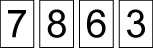
and Vincent took out
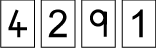
Who won? Why?
Then they played to make the highest odd number. Belinda took out
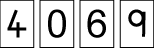
and Ali took out
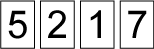
Who won? Why?
Next they played to make the lowest even number. Rohan took out

and Ben took out

Who won? Why?
The last game they played was to make the closest number to $5000$. Alice took out

and Chloe took out

Who won? Why?
Once you've played this game a few times, have a go at playing Nice or Nasty. This game is very similar except you draw and place the digits one at a time, so you'll need to think carefully about where to put each one!
Why do this problem?
Possible approach
At the end of the lesson the group can gather together to discuss, not only place value and comparing and ordering numbers, but also odd and even numbers. There should be plenty of opportunities to emphasise the appropriate vocabulary for the work they have been doing.
Key questions
Which digit is most important if you are making the largest/smallest number possible?
Possible extension
Learners could play an alternative version of the game in which two players take turns in taking a digit card (unseen) and placing it on their board before taking the next card. This requires considerable thought and understanding. Children will enjoy playing Nice and Nasty after having a go at this activity.
Possible support
Some children find place value difficult and even alarming. They could start with a similar activity using only three-digit numbers or even just two. Reading the numbers out loud may help turn what seems to them just a jumble of digits into something meaningful.
You may also like
Six Is the Sum
What do the digits in the number fifteen add up to? How many other numbers have digits with the same total but no zeros?
ABC
In the multiplication calculation, some of the digits have been replaced by letters and others by asterisks. Can you reconstruct the original multiplication?

