Skip over navigation
The problem was to find the largest integer which divides every member of the following sequence:
\[1^5-1,\ 2^5-2,\ 3^5-3,\cdots\ n^5-n.\]
The solution depends only on a little algebra and some clear mathematical thinking.
Pierre, Tarbert Comprehensive, Ireland, Prateek, Riccarton High School, Christchurch, New Zealand and Vassil from Lawnswood Sixth Form, Leeds started by taking small values of $n$, usually a good way to begin. This solution comes from Arun Iyer, S.I.A High School and Junior College, India. They all found the answer which is $30$.
Given the sequence $1^5-1,\ 2^5-2,\ 3^5-3,\cdots \ n^5-n$ we see that
\[n^5 - n = n(n^4 - 1) = n(n - 1)(n + 1)(n^2 + 1)\]
and it is quite easy to see that $n(n-1)(n+1)(n^2+1)$ is divisible by $2$, $3$ and $5$ for all values of $n$. As $n$, $(n-1)$ and $(n+1)$ are three consecutive integers their product must be divisible by $2$ and by $3$. If none of these numbers is divisible by $5$ then $n$ is either of the form $5k+2$ or $5k+3$ for some integer $k$ and in both of these cases we can check that $n^2 + 1$ is divisible by $5$. Since $2$, $3$ and $5$ are coprime therefore $n^5 - n$ is divisible by $2 \times 3 \times 5$ i.e by $30$.
Since the second term of the sequence is $2^5-2 = 30$ therefore the divisor cannot be greater than $30$. Therefore $30$ is the largest number that d ivides each member of the sequence.
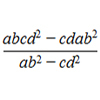
Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Common Divisor
Age 14 to 16
Challenge Level 





- Problem
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources
The problem was to find the largest integer which divides every member of the following sequence:
\[1^5-1,\ 2^5-2,\ 3^5-3,\cdots\ n^5-n.\]
The solution depends only on a little algebra and some clear mathematical thinking.
Pierre, Tarbert Comprehensive, Ireland, Prateek, Riccarton High School, Christchurch, New Zealand and Vassil from Lawnswood Sixth Form, Leeds started by taking small values of $n$, usually a good way to begin. This solution comes from Arun Iyer, S.I.A High School and Junior College, India. They all found the answer which is $30$.
Given the sequence $1^5-1,\ 2^5-2,\ 3^5-3,\cdots \ n^5-n$ we see that
\[n^5 - n = n(n^4 - 1) = n(n - 1)(n + 1)(n^2 + 1)\]
and it is quite easy to see that $n(n-1)(n+1)(n^2+1)$ is divisible by $2$, $3$ and $5$ for all values of $n$. As $n$, $(n-1)$ and $(n+1)$ are three consecutive integers their product must be divisible by $2$ and by $3$. If none of these numbers is divisible by $5$ then $n$ is either of the form $5k+2$ or $5k+3$ for some integer $k$ and in both of these cases we can check that $n^2 + 1$ is divisible by $5$. Since $2$, $3$ and $5$ are coprime therefore $n^5 - n$ is divisible by $2 \times 3 \times 5$ i.e by $30$.
Since the second term of the sequence is $2^5-2 = 30$ therefore the divisor cannot be greater than $30$. Therefore $30$ is the largest number that d ivides each member of the sequence.
You may also like
DOTS Division
Take any pair of two digit numbers x=ab and y=cd where, without loss of generality, ab > cd . Form two 4 digit numbers r=abcd and s=cdab and calculate: {r^2 - s^2} /{x^2 - y^2}.

