Skip over navigation
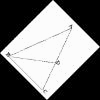
Consider the triangle $ABC$ as shown in the diagram. Use similar triangles to show that if $\angle B = 2 \angle A$ then $b^2=a^2+ac$.
To find integer solutions of this equation, consider the factors of $a(a+c)=b^2$, and that $a$ and $a+c$ have no common factors, so $a$ and $a+c$ must be perfect squares. This will lead to a parametric representation of $a$, $b$ and $c$ in terms of two parameters and you can use this to generate the triples.

Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Double Angle Triples
Age 16 to 18
Challenge Level 





- Problem
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
Consider the triangle $ABC$ as shown in the diagram. Use similar triangles to show that if $\angle B = 2 \angle A$ then $b^2=a^2+ac$.
To find integer solutions of this equation, consider the factors of $a(a+c)=b^2$, and that $a$ and $a+c$ have no common factors, so $a$ and $a+c$ must be perfect squares. This will lead to a parametric representation of $a$, $b$ and $c$ in terms of two parameters and you can use this to generate the triples.
You may also like
Two Trees
Two trees 20 metres and 30 metres long, lean across a passageway between two vertical walls. They cross at a point 8 metres above the ground. What is the distance between the foot of the trees?
Golden Triangle
Three triangles ABC, CBD and ABD (where D is a point on AC) are all isosceles. Find all the angles. Prove that the ratio of AB to BC is equal to the golden ratio.
Strange Rectangle
ABCD is a rectangle and P, Q, R and S are moveable points on the edges dividing the edges in certain ratios. Strangely PQRS is always a cyclic quadrilateral and you can find the angles.

