Skip over navigation
Article by Jennifer Piggott and Jo Scholten
This article discusses a small group of activities taken from the Mathematical Games Archive on the NRICH site. They all have a related structure that can be used to develop the skills of strategic thinking and reasoning as well as ideas of analogy and isomorphisms. Students at all levels of ability and age can access them. At the most basic level, they offer opportunities for practising arithmetical skills. At a higher level, they can be used to promote mathematical discussion by demanding detailed and reasoned explanations for a winning strategy, or an explanation of the mathematics that links the games.
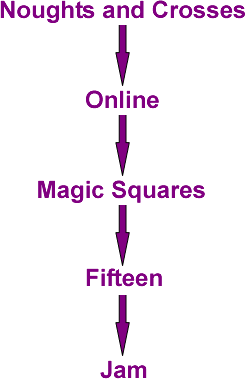
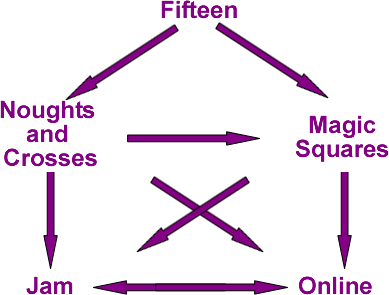
Several of the games link into one another. One suggestion is given below. Can you describe the similarities between all of these games?
Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Age 7 to 16
Published 2006 Revised 2013
Winning Lines
This article discusses a small group of activities taken from the Mathematical Games Archive on the NRICH site. They all have a related structure that can be used to develop the skills of strategic thinking and reasoning as well as ideas of analogy and isomorphisms. Students at all levels of ability and age can access them. At the most basic level, they offer opportunities for practising arithmetical skills. At a higher level, they can be used to promote mathematical discussion by demanding detailed and reasoned explanations for a winning strategy, or an explanation of the mathematics that links the games.
Suggested Progression
These games can be tackled in any order, but we suggest the order given below:

Links
Several of the games link into one another. One suggestion is given below. Can you describe the similarities between all of these games?
Links with the UK Framework
The following objectives are to be found in the Frameworks for teaching mathematics for Key Stages 1, 2 and 3, and apply to the activities in this theme.
- Solve mathematical problems or puzzles, recognise simple patterns and relationships, generalise and predict.
- Discuss the chance or likelihood of particular events.
- Use the language associated with probability to discuss events.
- Understand addition and subtraction mental calculation strategies.
- Represent problems mathematically.
- Explain and justify methods and conclusions.
- Recognise and visualise the transformation and symmetry of a 2-D shape.
- Use logical argument to establish the truth of a statement.
- Solve increasingly demanding problems and evaluate solutions.
- Present a concise, reasoned argument, using symbols, diagrams, graphs and related explanatory text.
- Suggest extensions to problems, conjecture and generalise.

Noughts and Crosses
Play the game on line. If you start, is it possible to guarantee that you will win the game? Try to explain the strategy. You might find diagrams helpful.
Online
Play the game on line. If you start, is it possible to guarantee that you will win the game? Try to explain the strategy using diagrams as appropriate.
Magic Squares
Try to complete the board given 4 of the 9 squares.
For a harder problem, you could try to complete the board given only the centre square.
For a harder problem still, you could try to complete the board given none of the squares. Here are some ideas to help you organise your thinking and extend your work on magic squares:
- The sum of the numbers 1 to 9 is linked to the row total- how?
- What magic totals are possible with consecutive numbers?
- Can you make magic squares from numbers that are not consecutive?
- Can you give any rules for making these magic squares?
This is a wonderful lead into generalisation and algebra.
For more ideas and further information, see these articles on the NRICH site:
In addition there are a number of problems based on magic squares which you can find by using the word search at the top of every page on the NRICH website.
Fifteen
Is it possible to win the game in 3 moves?
Can you devise a winning strategy?
Jam
You can play the game jam here .
Can you describe any similarities between this game, Noughts and Crosses and Online?
There are a number of articles on the site relating to using games in the classroom, they are:
Learning Maths Through Games I: Why games?
Learning Maths Through Games II: Types of games.
Learning Maths Through Games III: Creating your own games.
Learning Maths Through Games IV :From strategy games to investigations

