Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Product Sudoku



Product Sudoku printable worksheet
Product Sudoku printable worksheet for recording your journey
Product Sudoku printable worksheet to see a possible journey
By Henry Kwok
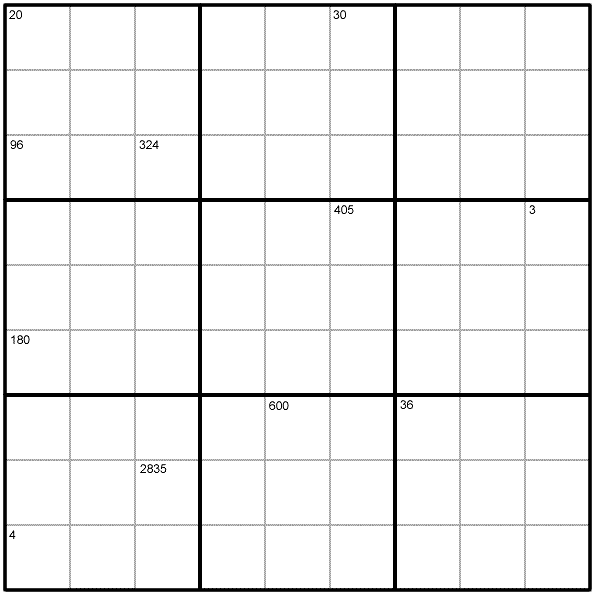
Rules of Product Sudoku
Like a conventional Sudoku, this Product Sudoku has two basic rules:
1. Each column, row and $3 \times 3$ subgrid must have the numbers 1 to 9.
2. No column, row or subgrid can have two cells with the same number.
The puzzle can be solved with the help of the numbers in the top parts of certain cells. These numbers are the products of the digits in all the cells horizontally and vertically adjacent to the cell.
A Short Demonstration
Related Collections
You may also like
Adding All Nine
Make a set of numbers that use all the digits from 1 to 9, once and once only. Add them up. The result is divisible by 9. Add each of the digits in the new number. What is their sum? Now try some other possibilities for yourself!
DOTS Division
Take any pair of two digit numbers x=ab and y=cd where, without loss of generality, ab > cd . Form two 4 digit numbers r=abcd and s=cdab and calculate: {r^2 - s^2} /{x^2 - y^2}.

