Skip over navigation
Any line which passes though the centre of the square divides the square into two congruent shapes. An example is shown below.
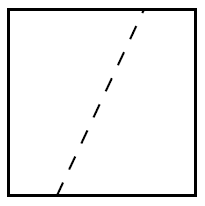
There are an infinite number of suitable lines (lines passing through the centre, at any angle) so there are infinitely many ways the square can be cut in half with a single straight cut.

Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Square Bisection
Age 11 to 14
ShortChallenge Level 





- Problem
- Solutions
Any line which passes though the centre of the square divides the square into two congruent shapes. An example is shown below.

There are an infinite number of suitable lines (lines passing through the centre, at any angle) so there are infinitely many ways the square can be cut in half with a single straight cut.
This problem is taken from the UKMT Mathematical Challenges.
You can find more short problems, arranged by curriculum topic, in our short problems collection.
You may also like
Square Areas
Can you work out the area of the inner square and give an explanation of how you did it?
2001 Spatial Oddity
With one cut a piece of card 16 cm by 9 cm can be made into two pieces which can be rearranged to form a square 12 cm by 12 cm. Explain how this can be done.

