Skip over navigation
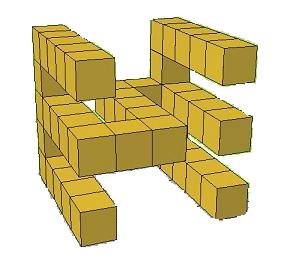
Then you can take away blocks, checking each face projection so its unchanged.
On the far E, you can take away 4 on the top prong, 4 on the bottom prong, and the 1 back block on the middle prong. The middle of the S cannot be removed as it is needed for the S face. The on the close E you can take 4 from the middle prong, and then the back block on the top and bottom prong.
So we have removed $15$ blocks, and you cannot remove any more. So the minimum total is $41-15=26$

Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
The Perforated Cube
Age 14 to 16
Challenge Level 





- Problem
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources
Edison from Shatin School included some edited versions of the diagram given in the hints to support his argument:
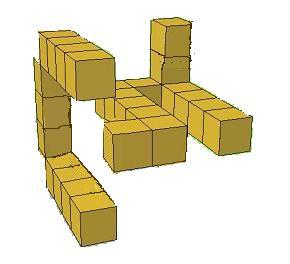
The most is 41 blocks, as is the picture in hints. Every block
you try and add will change of of the faces. So the maximum
is,
Then you can take away blocks, checking each face projection so its unchanged.
On the far E, you can take away 4 on the top prong, 4 on the bottom prong, and the 1 back block on the middle prong. The middle of the S cannot be removed as it is needed for the S face. The on the close E you can take 4 from the middle prong, and then the back block on the top and bottom prong.
So we have removed $15$ blocks, and you cannot remove any more. So the minimum total is $41-15=26$

Well done Edison, can anyone think of any other interesting projections to aim for?
You may also like
Just Rolling Round
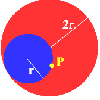
P is a point on the circumference of a circle radius r which rolls, without slipping, inside a circle of radius 2r. What is the locus of P?
Coke Machine
The coke machine in college takes 50 pence pieces. It also takes a certain foreign coin of traditional design...
Just Opposite
A and C are the opposite vertices of a square ABCD, and have coordinates (a,b) and (c,d), respectively. What are the coordinates of the vertices B and D? What is the area of the square?

