Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Ideal Axes



At constant temperature $T$, the gas law $PV=nRT$ is effectively an equation with two variables. Plotting different combinations of the variables $P$ and $V$ as the axes yields the three charts below. Can you deduce the likely variables and units for the axes in each case and the value for $nRT$? What is the likely physical interpretation of this value?
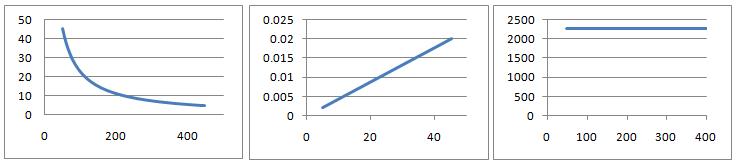
Explore the different possibilities for the shapes of graphs for the following equations by choosing different variables for the axes (you choose values for the constants)
Kinetic theory equations: Plot $PV = \frac{1}{3}mN\bar{c^2}$ for fixed $V$ and variable $P$, $\bar{c^2}$
van der Waals equations: Plot $(P+aV^{-2}_m)(V_m-b)=RT$ for fixed $T$ and variable $P$, $V_m$.
Can each be plotted in a form qualitatively similar to the three charts above? Can they be plotted to yield other forms distinct from the above?
You might wish to use a spreadsheet to allow you to make the various plots quickly, and you may wish to explore other formulas common to science.
You may also like
Power Up
Show without recourse to any calculating aid that 7^{1/2} + 7^{1/3} + 7^{1/4} < 7 and 4^{1/2} + 4^{1/3} + 4^{1/4} > 4 . Sketch the graph of f(x) = x^{1/2} + x^{1/3} + x^{1/4} -x

