Skip over navigation


Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Food Chains
Age 11 to 14
Challenge Level 





Here is a food chain:
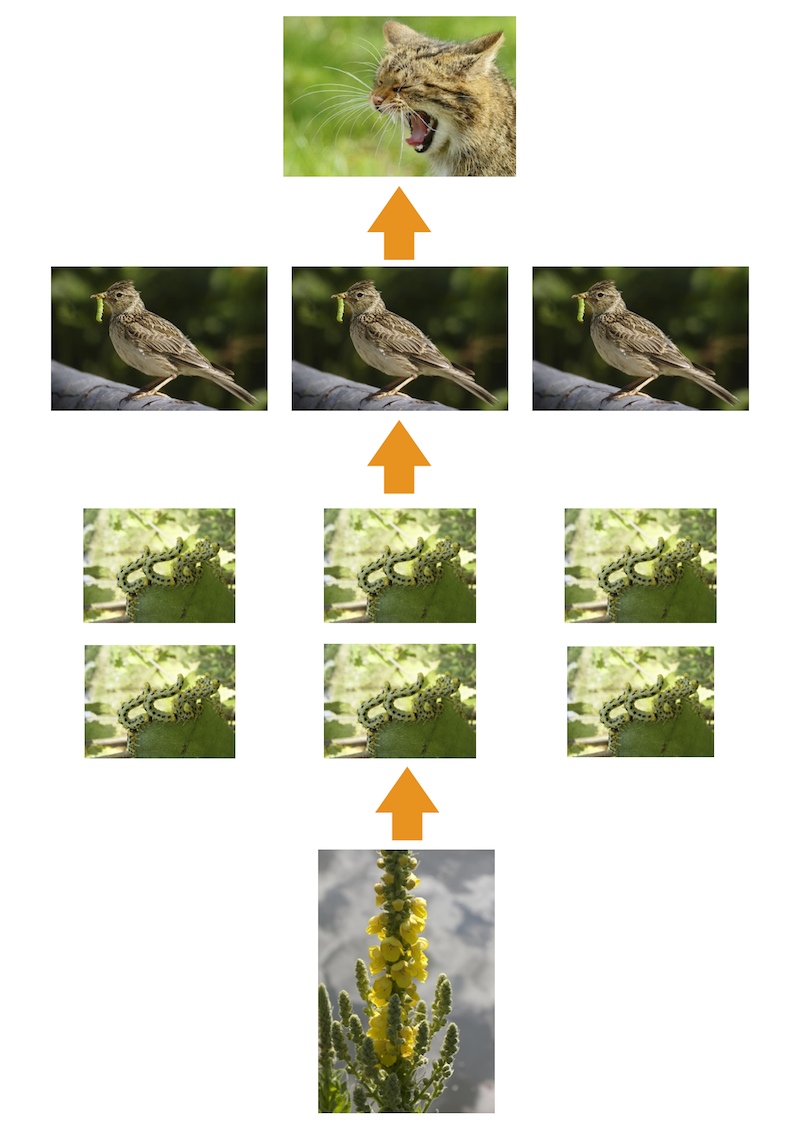
A wildcat will eat 3 birds every day. These three birds will eat 10 caterpillars each, every day, totaling 30 caterpillars. The 30 caterpillars will eat one small bush together every day.
a. In the area that these animals live in, the ecosystem can support 500 small bushes being eaten every day. Calculate the numbers of each animal in the food chain.
b. As you go up the food chain, the amount of energy available to the following predator decreases. For this food chain, the amount of energy available decreases by 25% for every level in the chain. Calculate how much more energy the wildcat could obtain from becoming a
vegetarian and eating the bush rather than from eating birds.
c. One year, a bacteria kills 5000 caterpillars. What effect will this have on the food chain?
d. Suppose that the wildcats decide to become vegetarians and eat bushes instead of other animals. How many wildcats could 500 bushes support (ignoring the other animals)?
e. If the wildcats became omnivorous (with some of them eating animals and some eating bushes), how many animals would there be if half of the bushes were eaten by caterpillars and the other half were eaten by wildcats?
e. If the wildcats became omnivorous (with some of them eating animals and some eating bushes), how many animals would there be if half of the bushes were eaten by caterpillars and the other half were eaten by wildcats?
You may also like
Speedy Sidney
Two trains set off at the same time from each end of a single straight railway line. A very fast bee starts off in front of the first train and flies continuously back and forth between the two trains. How far does Sidney fly before he is squashed between the two trains?
Air Nets
Can you visualise whether these nets fold up into 3D shapes? Watch the videos each time to see if you were correct.

