Skip over navigation

Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Tray Bake
Age 11 to 14
Challenge Level 





- Problem
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources
Start from the information given for 12 cakes.
12 cakes cost 65p.
For 24 cakes, double the cost is £1.30.
For 36 cakes, the cost of 12 cakes multiplied by 3 is £1.95.
For 6 cakes, half the cost is not 32.5p, since we no longer have half pence in the UK. The cost is therefore 33p.
For the ingredients:
To scale the recipe for other numbers of cakes which are not a simple multiple of 12 or 6, you will need to find the cost of 1 cake and the amount of ingredients required for 1 cake. Then multiply by the number of cakes required, rounding your answers sensibly and remembering that eggs come in whole numbers! (Professional kitchens weigh the eggs, rather than using whole numbers of eggs.)
If you are using the provided arrows, these facts may help you:
12 cakes cost 65p.
For 24 cakes, double the cost is £1.30.
For 36 cakes, the cost of 12 cakes multiplied by 3 is £1.95.
For 6 cakes, half the cost is not 32.5p, since we no longer have half pence in the UK. The cost is therefore 33p.
For the ingredients:
| Ingredients | 12 cakes | 24 cakes | 36 cakes | 6 cakes | 1 cake |
| Caster sugar | 130g | 260g | 390g | 65g | 10.8g |
| Margarine | 130g | 260g | 390g | 65g | 10.8g |
| Self raising flour | 130g | 260g | 390g | 65g | 10.8g |
| Eggs | 2 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 1/3 |
| Baking powder (5ml spoons) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1/2 | 1/12 |
To scale the recipe for other numbers of cakes which are not a simple multiple of 12 or 6, you will need to find the cost of 1 cake and the amount of ingredients required for 1 cake. Then multiply by the number of cakes required, rounding your answers sensibly and remembering that eggs come in whole numbers! (Professional kitchens weigh the eggs, rather than using whole numbers of eggs.)
If you are using the provided arrows, these facts may help you:
- use x2 (doubling) arrows going from 6 cakes to 12 and from 12 cakes to 24
- use divide by 2 or multiply by 1/2 (halving, same thing as division and multiplication are inverse processes,and 1/2 is the inverse of 2) arrows for 12 cakes to 6 or 24 cakes to 12
- use x 1.5 or x3/2 or half as much again cards going from 24 cakes to 36
- use divide by 1.5 or x2/3 cards going from 36 cards to 24
You may also like
Rule of Three
If it takes four men one day to build a wall, how long does it take 60,000 men to build a similar wall?
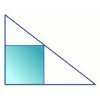
How Big?
If the sides of the triangle in the diagram are 3, 4 and 5, what is the area of the shaded square?

