Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Making Moiré Patterns



Moiré patterns are a type of interference pattern made when lines overlap.
Here are some examples of Moiré patterns:
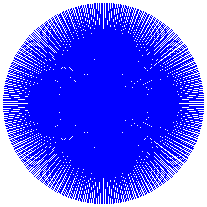

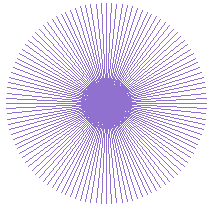
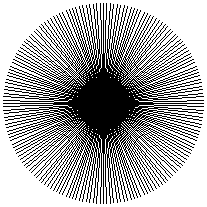
These patterns were created using LOGO.
Can you work out which LOGO commands give rise to each pattern?
- cs setpc 16 repeat 360 [fd 100 bk 100 rt 7 fd 25 bk 25 rt 5 fd 15 bk 15 rt 2] ht
- cs setpc 2 repeat 90 [fd 100 bk 100 rt 3 fd 100 bk 100 rt 1] ht
- cs setpc 13 repeat 360 [fd 100 bk 100 rt 7 fd 25 bk 25 rt 7 fd 10 bk 10 rt 7] ht
- cs setpc 1 repeat 360[fd 200 rt 1 bk 200 rt 1] ht
If you are unfamiliar with LOGO, click below to see a glossary of the terms used above.
setpc: set pen colour
fd: move turtle forward a specified distance
bk: move turtle back a specified distance
rt: right turn through an angle in degrees
lt: left turn through an angle in degrees
st: show turtle
ht: hide turtle
Try making some Moiré patterns of your own. Make changes to your LOGO code and see the effects you can create.
What do you notice?
Send us your examples of Moiré patterns, together with the LOGO code you used to generate them.
You can download free software for LOGO: FMSLogo for Windows, ACSLogo for Mac (user guide and tutorials).
You may also like
First Forward Into Logo 1: Square Five
A Short introduction to using Logo. This is the first in a twelve part series.
LOGO Challenge 1 - Star Square
Can you use LOGO to create this star pattern made from squares. Only basic LOGO knowledge needed.
LOGO Challenge 5 - Patch
Using LOGO, can you construct elegant procedures that will draw this family of 'floor coverings'?

