Skip over navigation




Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Tidying
Age 3 to 5
Counting, matching numerals and amounts
Calculating
Using shape properties
Calculating
Using shape properties





Children often enjoy hunting for missing items or counting to excitingly high numbers at tidy-up time
Adults could plan to focus on particular children to support and challenge, as well as intervening opportunistically.
The Activity
If resources are organised in containers with number labels showing how many there should be, then everyone can be involved in 'stock checks' to count and see if any are missing. 'Check point' number tracks help identify the missing number. Children can also match construction blocks or tools onto silhouettes, or numbered trikes to their parking bays.
If resources are organised in containers with number labels showing how many there should be, then everyone can be involved in 'stock checks' to count and see if any are missing. 'Check point' number tracks help identify the missing number. Children can also match construction blocks or tools onto silhouettes, or numbered trikes to their parking bays.
Encouraging mathematical thinking and reasoning:
Describing
How many are there altogether?
How do you know?
Do you notice anything about the bigger numbers?
How many are there altogether?
How do you know?
Do you notice anything about the bigger numbers?
Reasoning
How many more do we need?
Do you think we have the right number yet, with those two?
How did you know we would have the right number?
How many more do we need?
Do you think we have the right number yet, with those two?
How did you know we would have the right number?
Opening Out
What shape of box/basket/container do we need for these?
Is there a better way of doing this?
What shape of box/basket/container do we need for these?
Is there a better way of doing this?
Recording
Can you keep track on your clipboard of how many we have found?
Tell me about what you've written/drawn.
Can you keep track on your clipboard of how many we have found?
Tell me about what you've written/drawn.
The Mathematical Journey
Counting:
- saying one number for each object
- remembering the pattern of the number sequence
- understanding cardinality i.e. that the last number gives the total
Matching numerals and amounts:
- reading numerals with the purpose of seeing how many there should be
Subtraction:
- progressing from one more to bigger missing numbers
- using fingers, visualising or counting on (this is the aspect of subtraction called 'complementary addition' or 'inverse of addition' and involves seeing numbers as parts within wholes)
Shape properties:
- noticing similarities and differences, and matching the 2D face of an object to an outline or silhouette
Development and Variation
Children can help to organise, count and make the labels for resources in the classroom, outdoors or a role play area, such as a shop.
Labels showing different numbers, for example '10 pairs of scissors' or '110 pieces of Lego', can be used to differentiate challenges. Children can count as far as they can, just for fun. Number lines with numbers of dots under the numerals will help as a reference and giant 100 squares support counting to higher numbers.
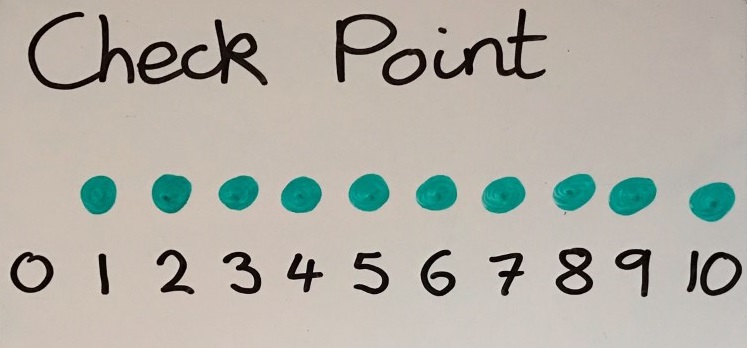 A number track is useful to count things onto. Children can identify the target number, count the objects onto the track, then count the empty spaces to find how many are missing. Objects can be placed on a 'checkpoint' of numbered spots (see photo).
A number track is useful to count things onto. Children can identify the target number, count the objects onto the track, then count the empty spaces to find how many are missing. Objects can be placed on a 'checkpoint' of numbered spots (see photo).
Children can use calculators to support counting, like a clicker tally, by pressing + 1 =, then pressing = each time they count a new item.
Children can help to organise, count and make the labels for resources in the classroom, outdoors or a role play area, such as a shop.
Labels showing different numbers, for example '10 pairs of scissors' or '110 pieces of Lego', can be used to differentiate challenges. Children can count as far as they can, just for fun. Number lines with numbers of dots under the numerals will help as a reference and giant 100 squares support counting to higher numbers.
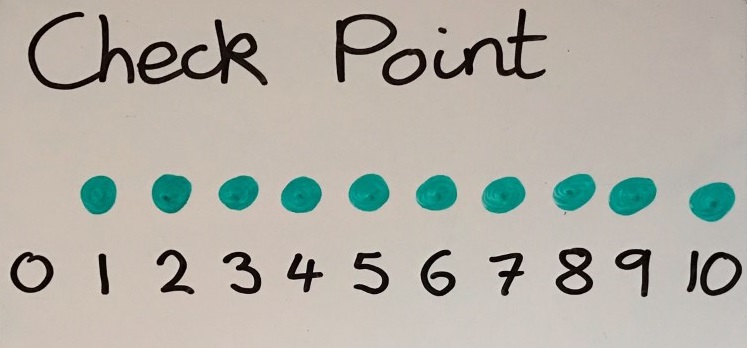 A number track is useful to count things onto. Children can identify the target number, count the objects onto the track, then count the empty spaces to find how many are missing. Objects can be placed on a 'checkpoint' of numbered spots (see photo).
A number track is useful to count things onto. Children can identify the target number, count the objects onto the track, then count the empty spaces to find how many are missing. Objects can be placed on a 'checkpoint' of numbered spots (see photo).Children can use calculators to support counting, like a clicker tally, by pressing + 1 =, then pressing = each time they count a new item.
Resources
Labelled containers.
Number tracks or 'checkpoints'.
Illustrated number lines and giant 100 squares.
Calculators.
Labelled containers.
Number tracks or 'checkpoints'.
Illustrated number lines and giant 100 squares.
Calculators.
Download a PDF of this resource.
Acknowledgement: Janine Davenall


