Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Missing Multipliers



- Problem
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources
Joey from St Theresa's Catholic College in Australia and Aditya from St Columbas College in the UK sent in completed grids. This is Aditya's work (click here here to see a bigger version):

| Janeen from Westridge School in America only needed to reveal six answers: |
Rhihito from the American School in Japan sent in this result: |
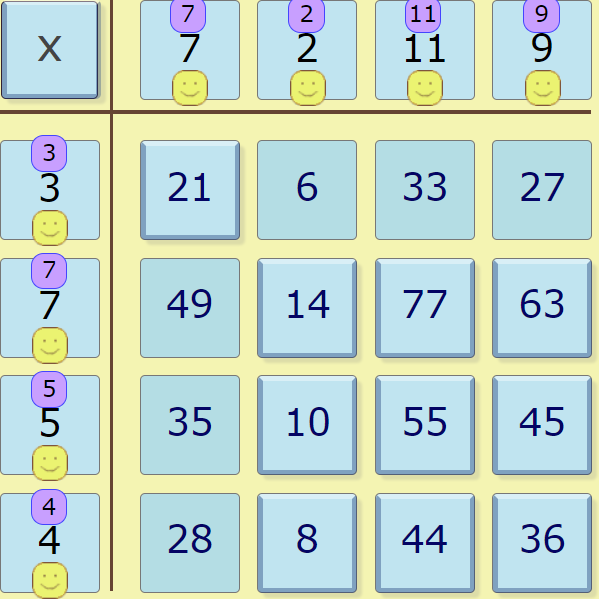
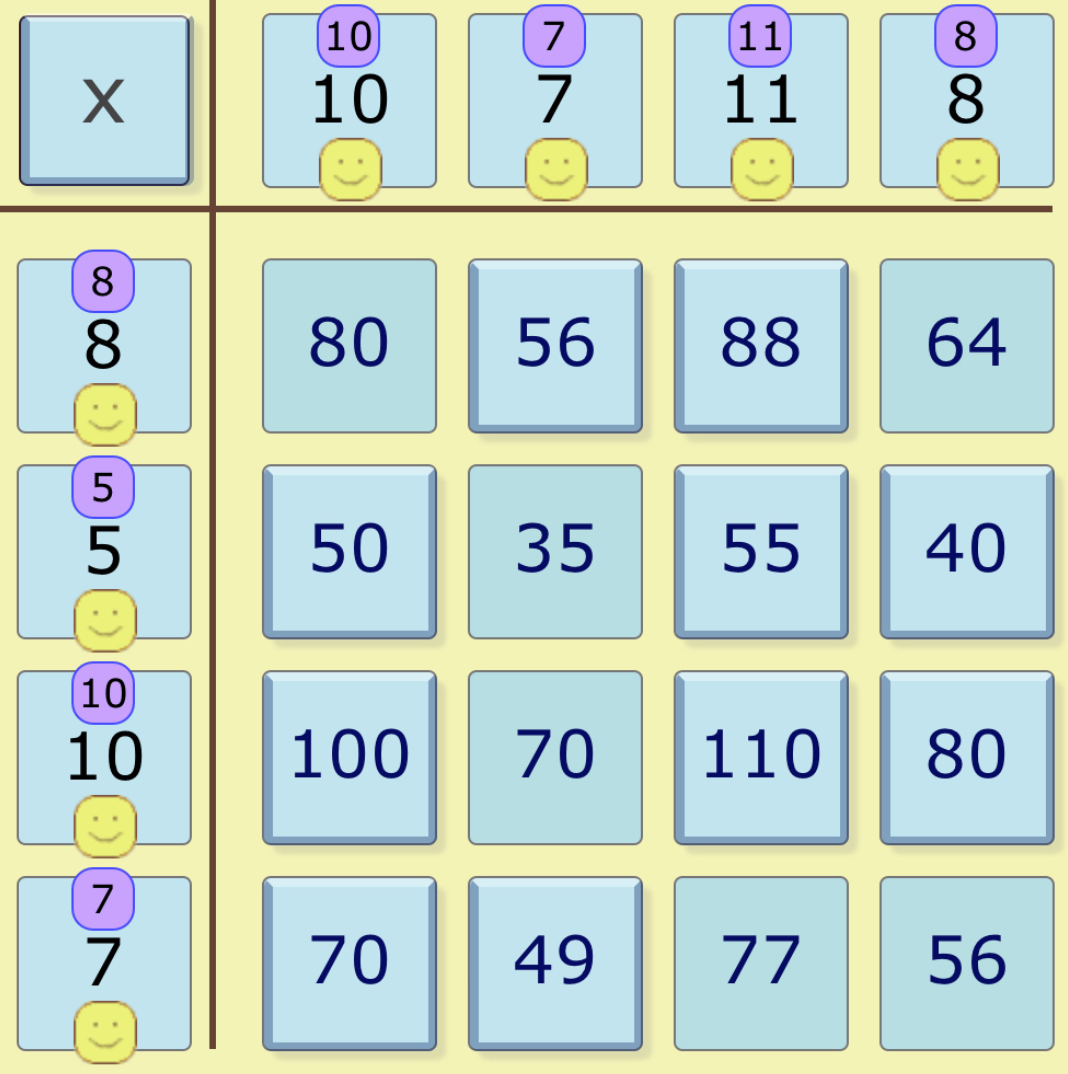
Keshav from Colchester Royal Grammar School and Anh Minh from the British Vietnamese International School, Hanoi in Vietnam described a general method revealing seven squares. This is Keshav's work:
You have to reveal at least seven squares to find all the headings.
Firstly, reveal any square you want. Then, reveal any other square next to it (horizontally or vertically). Using your knowledge of factors, you can then find the heading of that row.
Then, reveal a square next to either of the two that are already revealed, and make sure that square doesn't belong to the heading that you've already figured out.
Now you have two headings. You can use these two headings to find all the others, still using your knowledge of factors, using just the row and column you've formed.
Could Janeen's method be described in this way?
Tuấn Vé from the British Vietnamese International School in Hanoi described a method for larger grids. How could you use what we've seen here to make this method more efficient?
You need to know at least two values of each row to solve the problem, you will need to open it in two vertical lines. So you will need 2$y$ if the table is $y \times y$.
So for 4$\times$4 you need to open 8 values; for 6$\times$6 you need 12;for 8$\times$8 you need 16 and so on.
That's not quite right, since Keshav's method for a 4 by 4 grid uses 7 values, and Janeen's uses 6.
In fact, one in each row and one in each column means $y\times y-1$ because the row and column will cross.
As Janeen noticed, you don't actually need the sqaure in the row and column, because you can find both of those headings from the other rows. So in fact you need to reveal $y\times y-2$ reveals.
Related Collections
You may also like
Pebbles
Place four pebbles on the sand in the form of a square. Keep adding as few pebbles as necessary to double the area. How many extra pebbles are added each time?
It Figures
Suppose we allow ourselves to use three numbers less than 10 and multiply them together. How many different products can you find? How do you know you've got them all?
Bracelets
Investigate the different shaped bracelets you could make from 18 different spherical beads. How do they compare if you use 24 beads?

