Skip over navigation

Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Lattice Points
Age 16 to 18
Challenge Level 





- Problem
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources
The idea for this problem came from a Note in the Mathematical
Gazette, Volume 20, July 2006 by Thomas Koshy entitled 'Lattice
points in a family of hyperbolas'.
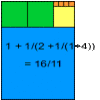
Even if you find some lattice points by trial and error you will still have to prove that there are no other possibilities.
Even if you find some lattice points by trial and error you will still have to prove that there are no other possibilities.
You may also like
Shades of Fermat's Last Theorem
The familiar Pythagorean 3-4-5 triple gives one solution to (x-1)^n + x^n = (x+1)^n so what about other solutions for x an integer and n= 2, 3, 4 or 5?
BT.. Eat Your Heart Out
If the last four digits of my phone number are placed in front of the remaining three you get one more than twice my number! What is it?

