Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Dotty Circle



- Problem
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources
Dotty Circle
Watch the film below.
Try to describe what happens in the film to someone else.
Imagine the dot starts at the point (1,0), turns through $20^\circ$ and then stops:
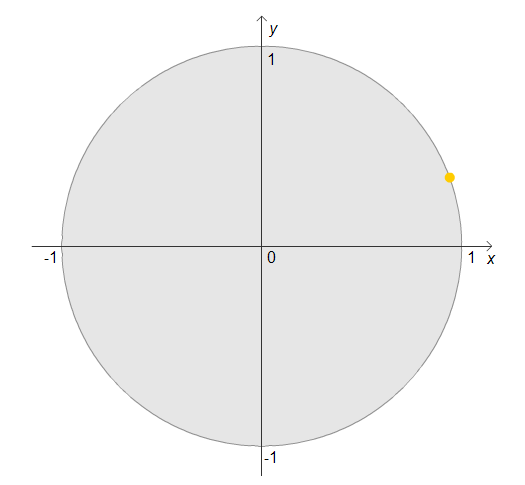
If the point now carries on, through how many degrees must it turn to finish the same height above or below the horizontal axis as it was when it had gone through $20^\circ$?
Can you find a general rule for explaining when the dot will be this same distance from the horizontal axis?
You might like to try Round and Round and Round after this problem.
The following is an extract from the notes provided by Alf Coles on his site, which was the insipration for this problem:
"I am aware of wanting to create a sense of drama and performance before showing a film. I make myself as still as I can and offer a minimum of context save that the task, having watched the film, will be to try and re-create together what we saw. However, students should not worry about trying to remember it, but just be present in what they see.
As the film finishes I am again aware of wanting to make myself as still as possible, pausing for as long as possible and speaking as slowly as I can. 'We are now going to try and re-construct what we saw. We will all have lots of images in our heads and images will be sparked off by what others say. Before we start sharing these images, there is one rule. When someone is talking your task is to
try and see what they say and, as much as you can, to let go of your own images in order to do that ... Okay, could someone offer us an image from the very beginning of the film. What did you see?'
One rule I give myself is not to speak second. With many groups the second speaker will not make a comment related to the first. If this happens I will remind the group of the rule and invite a comment about what the first speaker said.
I am not sure it is possible to say much more about working with film (and I have possibly said too much already) except to try it out!"
This particular problem is a great context in which to generalise and by that, we do not necessarily mean the use of algebraic expressions at this level. Encourage pupils to put into words the symmetry that they see, using what they know about the number of degrees in a circle - this is an equally valid way to generalise.
This activity is great for laying foundations for trigonometry, even though this is a topic which pupils will not officially meet until much later. To extend the ideas in this problem, your class could try A Quarter of a Million Degrees .
You may also like
Counting Counters
Take a counter and surround it by a ring of other counters that MUST touch two others. How many are needed?
Cuisenaire Squares
These squares have been made from Cuisenaire rods. Can you describe the pattern? What would the next square look like?
Doplication
We can arrange dots in a similar way to the 5 on a dice and they usually sit quite well into a rectangular shape. How many altogether in this 3 by 5? What happens for other sizes?

