Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Matching Triangles



- Problem
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources
Matching Triangles
These triangles belong to three different families.
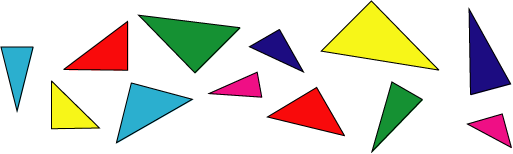
All the triangles in the same family are the same shape.
But they may not be the same size or the same way up.
Can you sort them out and explain how you did it?
You could print off pictures of the triangles (here as a Word document or here as a pdf), then cut them out and sort them practically. Or if you prefer, you could use the interactivity below to try out your ideas:
Why do this problem?
This activity is a good one to try with young children once they are familiar with the properties of a triangle. Often, they associate the name 'triangle' with a shape in a particular orientation and this problem is an excellent way to challenge this assumption. Other children may dismiss all three-sided shapes as triangles without looking at their other attributes. The activity will require pupils to look carefully at each shape and scrutinise its properties.
Possible approach
You could start by asking the group to tell you what they know about triangles. You could then ask one child to draw a triangle on the board and ask someone else to draw a different triangle. Invite the group to talk about what is the same and what is different about them. In this way, the discussion will include shape, size and orientation, but you could draw some triangles yourself to bring out certain aspects.
Next you could project the interactivity onto the interactive whiteboard, or show them the triangles on these sheets. (The first page has the triangles in colour, the second in black and white so that it can be photocopied.) Introduce the task and encourage the group to work in pairs with a set of cut-out triangles so that they are able to talk through their ideas with a partner. Listening to their justifications can reveal a lot about their understanding of similar triangles, even though this terminology is not used.
You can draw the class together for mini plenaries, as appropriate, perhaps to share misunderstandings or ways of working. You may wish to use the interactivity for drawing attention to particular triangles (it does not allow you to rotate the triangles). Once the majority of pairs have grouped their triangles in some way, invite the class to wander around the room looking at the arrangements. What do they notice? Do they have any questions? The interactivity could be used again to re-create a solution.
Key questions
Possible extension
Children could draw their own families of triangles and label the differences and similarities.
Possible support
Use one of these sheets so that the triangles can be cut out, then rotated and placed on top of one another. (The first page has the triangles in colour, the second in black and white.)
You may also like
Let's Investigate Triangles
Vincent and Tara are making triangles with the class construction set. They have a pile of strips of different lengths. How many different triangles can they make?

