Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Difference Sudoku



Difference Sudoku printable worksheet
By Henry Kwok
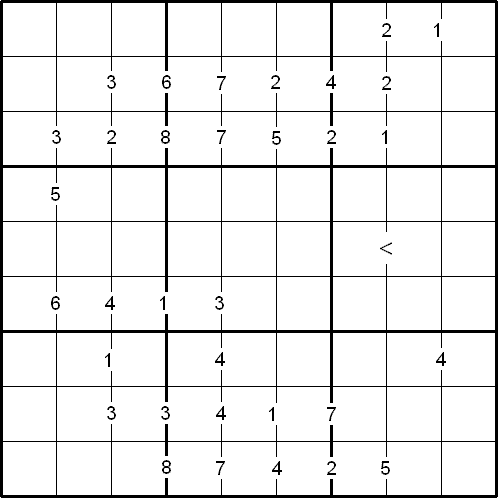
Rules of Difference Sudoku
Like the standard Sudoku, the object of the puzzle is to fill the whole $9 \times 9$ grid with numbers from $1$ to $9$, so that each row, each column, and each of the nine $3 \times 3$ squares contain all nine digits.
There are special clue-numbers placed on the border lines between selected pairs of adjacent squares of the grid. Each clue-number is the difference between the two numbers in the adjacent squares.
For example, a clue-number $7$ on the border line between two adjacent squares means that the possible pairs of numbers for the squares on either side must be one of the following combinations: $1$ and $8$, $8$ and $1$, $2$ and $9$, or $9$ and $2$.
The inequality sign indicates that the number in row 5 column 7 is smaller than the number in row 5 column 8.
As this variant has only one inequality sign on the border line, it is called Minimal Difference Sudoku.
Related Collections
You may also like
Two and Two
How many solutions can you find to this sum? Each of the different letters stands for a different number.


