Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Real-life Equations



- Problem
- Teachers' Resources
This is a list of many of the most important equations in science. In each case, we have labelled the two variable quantities $x$ and $y$. The letters $a, b$ stand for constants in each case
Constant motion $\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad a = \frac{x}{y}$
Constant acceleration $\quad\quad\quad x = uy + \frac{1}{2} ay^2$
Beer Lambert Law $\quad\quad\quad\quad a=bxy$
Exponential decay $\quad\quad\quad\quad x=a e^{by}$
Michaelis-Menton $\quad\quad\quad\quad x = \frac{ay}{b+y}$
pH $\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad x = -\log_{10}(y)$
Can you identify the possible meanings of the variables $x$ and $y$ and the constants in each case?
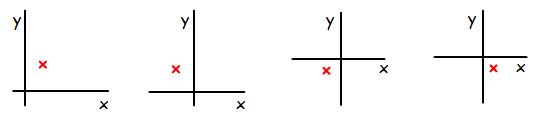
Four graphs are shown above, where the two axes intersect at the origin $(0, 0)$.
The red crosses show four measurements. Although we do not know the numerical values (because there are no scales on the graphs), we can see whether the values are positive or negative in each variable. For example, the first measurement is positive in $x$ and positive in $y$; the second measurement is positive in $y$, negative in $x$.
For processes evolving according to each of the equations above, which measurements are possible?
You may also like
Maths Shop Window
Make a functional window display which will both satisfy the manager and make sense to the shoppers

