Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Lennard Jones Potential



At a simple level, two interacting neutral atoms are subject to two opposing forces: firstly, they are weakly attracted by van der Waals forces; secondly they are repelled by Pauli repulsion. It is known that the van der Waals forces decay proportional to the sixth power of the separation and that the effects of the Pauli repulsion decay exponentially.
In 1924 it was suggested by Lennard and Jones that the potential energy of a system of two atoms separated by a distance $r$ could be approximated by
$$V(r) = 4\epsilon\left[\left(\frac{\sigma}{r}\right)^{12}-\left(\frac{\sigma}{r}\right)^6\right]$$
where $\epsilon$ and $\sigma$ are constants which are determined experimentally.
Think about this expression. What features might make it a sensible candidate for a model of reality?
A pair of atoms are brought together and the interaction energy measured. The results are plotted in the following chart:
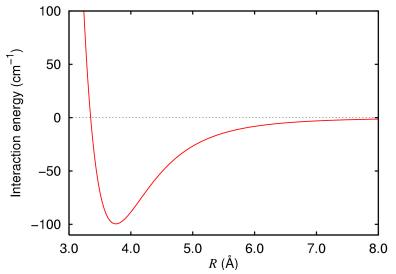
Experiment with the constants to determine how well the Lennard-Jones potential can be used to model this potential energy.
Suppose that another potential energy curve $W(r)$ was suggested as follows:
$$W(r) = 4\epsilon_w\left[\left(\frac{\sigma_w}{r}\right)^{9}-\left(\frac{\sigma_w}{r}\right)^6\right]$$
How does $W(r)$ differ from the Lennard Jones potential? Do you think that $W(r)$ could yield a good match with reality with a good choice of constants $\epsilon_w$ and $\sigma_w$?
John Lennard-Jones is considered to be the father of computational chemistry. This form of the potential has little theoretical justification, but sometimes matches reality to an acceptable standard. Its use greatly simplifies numerical calculations based on the inter-atomic potential.
Image taken from http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Argon_dimer_potential.png
You may also like
A Method of Defining Coefficients in the Equations of Chemical Reactions
A simple method of defining the coefficients in the equations of chemical reactions with the help of a system of linear algebraic equations.
Mathematical Issues for Chemists
A brief outline of the mathematical issues faced by chemistry students.
Reaction Rates
Explore the possibilities for reaction rates versus concentrations with this non-linear differential equation

