Skip over navigation
Peter from Durham Johnston School wrote:
1) The rule is the difference between the last two numbers in the sequence +1 added onto the previous number = the next number in the sequence.
X = the number you are trying to find, Y and Z = the past two numbers.
Z is the previous number that is before the number you are trying to find.
A = The difference between Z and Y
The difference between Z and Y + 1 = A .
A + 1 + Z = X
To put this into a real situation:
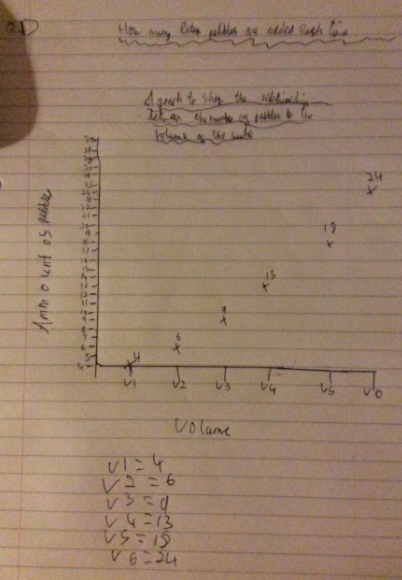
Sequence: 4, 6 , 9 , X
9 - 6 = 3
9 + 3 + 1 = X = 13
This then continues using the same rule. Below is a graph to show the relationship between the volume and amount of pebbles.
2) The rule is the difference between the previous two numbers in the sequence + 2 + the previous number = the next number in the sequence.
X = The number you are trying to find.
Y and Z = the previous two numbers in the sequence.
The difference between Z and Y = A
A + 2 + Z = X
3) It is always going to be 0.
4) The rule is the same as Q 2.
Zach sent in a very thorough explanation. You can view it in full here: More Pebbles - Zach T.pdf and it starts off like this:

Thank you for these solutions to what was really a tough nut to crack. Well done!


Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
More Pebbles
Age 7 to 11
Challenge Level 





- Problem
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources
Peter from Durham Johnston School wrote:
1) The rule is the difference between the last two numbers in the sequence +1 added onto the previous number = the next number in the sequence.
X = the number you are trying to find, Y and Z = the past two numbers.
Z is the previous number that is before the number you are trying to find.
A = The difference between Z and Y
The difference between Z and Y + 1 = A .
A + 1 + Z = X
To put this into a real situation:
Sequence: 4, 6 , 9 , X
9 - 6 = 3
9 + 3 + 1 = X = 13
This then continues using the same rule. Below is a graph to show the relationship between the volume and amount of pebbles.
2) The rule is the difference between the previous two numbers in the sequence + 2 + the previous number = the next number in the sequence.
X = The number you are trying to find.
Y and Z = the previous two numbers in the sequence.
The difference between Z and Y = A
A + 2 + Z = X
3) It is always going to be 0.
4) The rule is the same as Q 2.

Zach sent in a very thorough explanation. You can view it in full here: More Pebbles - Zach T.pdf and it starts off like this:

Thank you for these solutions to what was really a tough nut to crack. Well done!
You may also like
Consecutive Numbers
An investigation involving adding and subtracting sets of consecutive numbers. Lots to find out, lots to explore.
Tea Cups
Place the 16 different combinations of cup/saucer in this 4 by 4 arrangement so that no row or column contains more than one cup or saucer of the same colour.
Tiles on a Patio
How many ways can you find of tiling the square patio, using square tiles of different sizes?

