Skip over navigation


Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Maximum Flow
Age 16 to 18
Challenge Level 





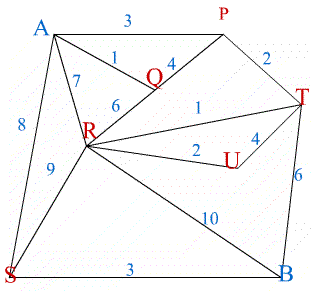
The graph represents a supply network from $A$ to $B$ and the numbers on the edges of the graph show the maximum capacity for flow in each of the sections.
Imagine any straight line cutting through edges of the graph (but not through vertices) such that $A$ is on one side of the line and $B$ is on the other. All the flow from $A$ to $B$ has to go along the edges cut by your line so the total flow from $A$ to $B$ is less than or equal to the sum of the flows along those edges. Considering all possible such cuts, why is it that the maximum flow
from $A$ to $B$ is less than the minimum sum for all cuts? Find the maximum flow in this example.

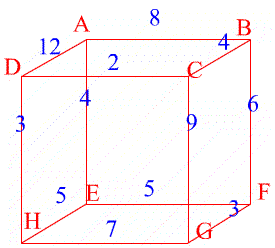
In the second example the network is a cube. Find the maximum flow from $A$ to $G$.
You may also like
Instant Insanity
Given the nets of 4 cubes with the faces coloured in 4 colours, build a tower so that on each vertical wall no colour is repeated, that is all 4 colours appear.
Network Trees
Explore some of the different types of network, and prove a result about network trees.
Magic Caterpillars
Label the joints and legs of these graph theory caterpillars so that the vertex sums are all equal.

