Skip over navigation

Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Whose Line Graph Is it Anyway?
Age 16 to 18
Challenge Level 





- Problem
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources

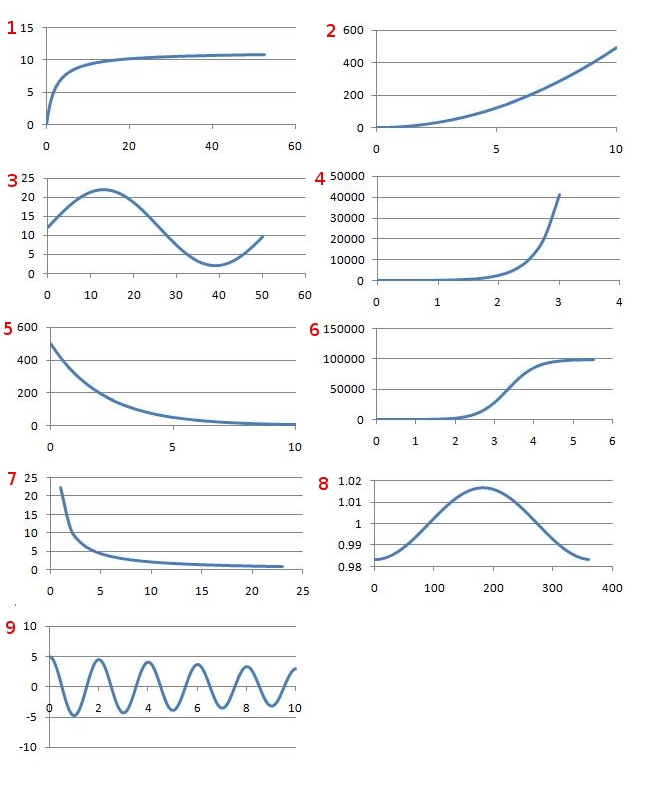
| Process | Graph | Equation | Explanation |
| 1 | 6 | H | In a food-limited environment bacteria tend to maximum number after initial exponential growth (following lag phase) |
| 2 | 5 | B | Concentration will exponentially decay as drug is metabolised |
| 3 | 9 | E | Pendulum will have an sinusodial motion with a decaying amplitude due to damping from air resistance |
| 4 | 7 | I | Ideal gas equation $pV = nRT$ therefore pressure and volume are in a reciprocal relationship |
| 5 | 2 | A | Ball is small and heavy, therefore assume air resistance is negligible at first and so acceleration is constant. $s = ut + \frac{1}{2}at^2$ therefore for $u=0;\ a=g \Rightarrow s=\frac{1}{2}gt^2$ (qualitatively vertical speed represented by gradient of graph is increasing) |
| 6 | 1 | F | As concentration of reagent increases so does reaction rate, however as increase continues concentration of the catalyst becomes the limiting factor (saturation) |
| 7 | 4 | G | When not food limited, bacteria follow exponential growth after initial lag phase |
| 8 | 3 | D | Hours of daylight varies from a maximum at mid-summer to minimum at mid-winter, with a mean value of 12 |
| 9 | 8 | C | Earth's orbit is not perfectly circular therefore small oscillations about mean distance (1 AU) with period of one year (note non-zero origin on vertical axis) |
You may also like
Power Up
Show without recourse to any calculating aid that 7^{1/2} + 7^{1/3} + 7^{1/4} < 7 and 4^{1/2} + 4^{1/3} + 4^{1/4} > 4 . Sketch the graph of f(x) = x^{1/2} + x^{1/3} + x^{1/4} -x

