Skip over navigation
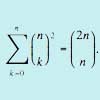

Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Particularly General
Age 16 to 18
Challenge Level 





- Problem
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources
Expand out the brackets in a systematic, organised manner.
You will need to use a double angle trig formula and difference of two squares. Considering $n=1$ might be useful.
There is perhaps no need to provide a proof for your identities if you are very clear in your mind how such a proof would be constructed, although you might wish to produce a proof if interested.
You may also like
Binomial
By considering powers of (1+x), show that the sum of the squares of the binomial coefficients from 0 to n is 2nCn
Powerful Factors
Use the fact that: x²-y² = (x-y)(x+y) and x³+y³ = (x+y) (x²-xy+y²) to find the highest power of 2 and the highest power of 3 which divide 5^{36}-1.

