Skip over navigation

Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Exploring Cubic Functions
Age 14 to 18
Challenge Level 





- Problem
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources
When working with functions and their graphs, here are a few key points to look out for:
Where does the graph cross the $x$ axis? (We call these the roots of the function)
Where does it cross the $y$ axis?
Does the graph have any reflectional or rotational symmetry?
Does the graph have any turning points?
Sketching Graphs - Transformations includes a video about the relationship between functions whose graphs are translations of each other.
When using the GeoGebra applets it might be a good idea to start the slider(s) at 0.
When you have two sliders, you could start by exploring the effect of moving each separately before exploring the effect of moving both together.
Where does the graph cross the $x$ axis? (We call these the roots of the function)
Where does it cross the $y$ axis?
Does the graph have any reflectional or rotational symmetry?
Does the graph have any turning points?
Sketching Graphs - Transformations includes a video about the relationship between functions whose graphs are translations of each other.
When using the GeoGebra applets it might be a good idea to start the slider(s) at 0.
When you have two sliders, you could start by exploring the effect of moving each separately before exploring the effect of moving both together.
You may also like
Cubic Spin
Prove that the graph of f(x) = x^3 - 6x^2 +9x +1 has rotational symmetry. Do graphs of all cubics have rotational symmetry?
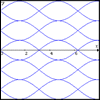
Sine Problem
In this 'mesh' of sine graphs, one of the graphs is the graph of the sine function. Find the equations of the other graphs to reproduce the pattern.
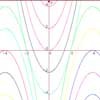
Parabolic Patterns
The illustration shows the graphs of fifteen functions. Two of them have equations y=x^2 and y=-(x-4)^2. Find the equations of all the other graphs.

