Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Triangle in a Trapezium



- Problem
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources
Why do this problem?
Students often think that there is only one correct way to approach a geometrical challenge. In this problem, students have the opportunity to discover a geometrical relationship, and then explore three starting points that lead to different methods to prove the relationship always holds. Along the way there's a chance for some "purposeful practice" at finding the area of triangles and trapezia.
Possible approach
Students may find it useful to work on dotty paper or use the dotty grids environment to explore the first part of this problem.
Start by showing the two trapeziums below, and explain that the triangles join the vertices of one of the non-parallel sides to the midpoint of the opposite side.
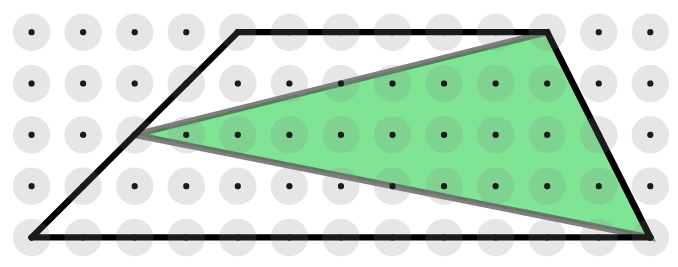
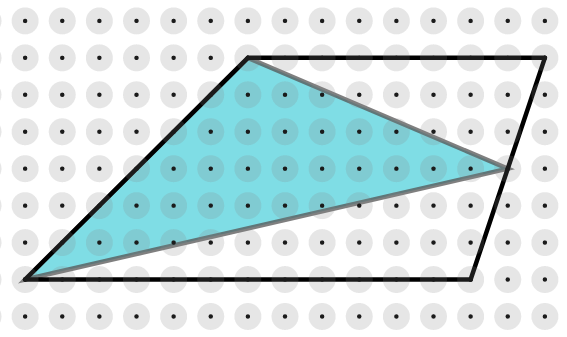
Invite students to work out the area of each trapezium and shaded triangle, and then discuss how they worked out the areas. Then ask them to draw some more trapeziums and construct triangles inside them in the same way. After everyone has had time to create some examples, collect together their results in a table on the board.
"What do you notice about the area of the triangle compared with the area of the trapezium?"
"It's always half the area!"
Invite students to think about how they could prove that the area of the triangle is always half the area of the trapezium. After they have had some time to think about it, you could hand out this worksheet: Triangle In a Trapezium. Challenge them to take each starting point and turn it into a complete justification. There are three different starting points so each group could work on a different starting point and then present the complete proof to the whole class. Finally, take time to discuss which method they found most convincing or appealing, and why.
Key questions
Starting Point 1
How would you work out the area of the two unshaded triangles?
Does it help to choose letters to represent some of the lengths and heights?
Using the same letters, can you work out the area of the trapezium?
Starting Point 2
How does triangle BEG compare with triangle AEF? How do you know?
How do we know that triangle CED and triangle CFD have the same area?
Starting Point 3
Can you prove that ABGH is a parallelogram?
Does it help to mark angles that you know are equal, and angles that you know add up to $180^{\circ}$?
Possible support
To scaffold the step from particular cases to the general proof, invite students to create the images from each Starting Point on dotty paper for trapezia that they have already explored. Then encourage them to adapt the reasoning from their numerical examples to prove the general case.
Possible extension
Kite in a Square is a more challenging geometrical problem which offers three different jumbled up proofs for students to sort out.
You may also like
Fitting In
The largest square which fits into a circle is ABCD and EFGH is a square with G and H on the line CD and E and F on the circumference of the circle. Show that AB = 5EF. Similarly the largest equilateral triangle which fits into a circle is LMN and PQR is an equilateral triangle with P and Q on the line LM and R on the circumference of the circle. Show that LM = 3PQ
Triangle Midpoints
You are only given the three midpoints of the sides of a triangle. How can you construct the original triangle?

