Skip over navigation
Article by Jennie Pennant and the NRICH team
Becoming confident and competent as a problem solver is a complex process that requires a range of skills and experience. As teachers we can support this process in three principal ways:
NRICH offers a wide range of rich tasks to engage learners in the problem-solving process. We want all our tasks to be used in such a way that they enable learners to explore and work from their own level of understanding, and then build on this towards new understandings. We believe that this approach offers the opportunity for rich, embedded learning.
Some of our NRICH tasks are simple games that can be played time and time again to develop numerical fluency as well as problem solving and reasoning, such as Spiralling Decimals and Totality (see also our article Developing Number Fluency - What, Why and How), whilst others may be non-routine problems that have a specific solution, such as Shape Times Shape. Some may take a short time, like Shut the Box, whilst others may intrigue and challenge over more than one lesson, like Dice in a Corner.
The key is to be clear how you want to use a particular problem to support the development of the children's skills to problem solve. It is tempting to choose a problem that relates to the mathematical content that you have been working on in class. However, whilst children need to be fluent with the mathematical content demands of any problem they tackle, it may be more productive to choose a problem that builds on a specific element of problem solving that you are working on as a class, and uses content that they are very familiar, and more confident, with.
The Primary National Strategy (May 2004) suggested that there are five different types of problem:
The stages of the problem-solving process
The problem-solving process can usually be thought of as having four stages:
We can helpfully spend time with children concentrating on one of these stages explicitly, in turn, as they learn to become confident problem solvers.
Stage 1: Getting started will mean offering them strategies to help them engage with the problem. These could be prompts such as:
The children will benefit from becoming proficient in each of these skills and working on one of them as a key focus in a lesson or series of lessons could be a useful strategy. Our article Using NRICH Tasks to Develop Key Problem-solving Skills offers further guidance.
Stage 3: Digging deeper usually happens when the problem has been explored and then it is possible to look for generalisations and proof. Here's an example from our NRICH problem Make 37:

Stage 4: Reflecting is the part of the problem-solving process where we support the children to:
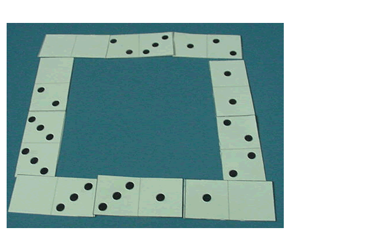
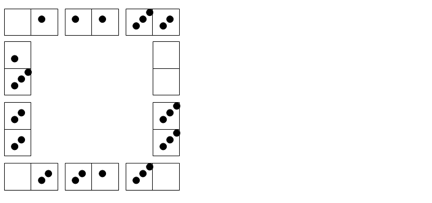
Written recording could be in the form of a photograph, diagram or written explanation. Here are some children's solutions to our NRICH problem Domino Square that illustrate how recording may develop:

Children will need support to develop their proficiency with written recording. Here's an example of a child explaining their thinking for Eggs in Baskets. She has used a trial and improvement approach.

You can read more about types of recording in this article.
As children reflect on the problem-solving adventure, they will need to be supported to compare different strategies that were used to solve the problem in order to consider the efficiency of the method and the elegance of the solution. This will enable them to see how they might refine their own methods or adopt a different one next time they encounter a similar problem.
The skills needed for a problem-solving task
By this we mean the problem-solving skills listed above in Stage 2: working on the problem. It will help the children become fluent in these if you take every opportunity to explicitly talk about them and use the appropriate language when they occur in games or larger problem-solving activities. You may like to focus on developing one or two at a time. The article Using NRICH Tasks to Develop Key Problem-solving Skills unpicks what we mean by these skills and draws attention to activities which will help learners develop them.
Our youngest learners can start thinking about 'working systematically' in contexts such as choosing two toppings out of sprinkles, sugar stars or flakes to go on top of iced biscuits they are making. The key question is - 'how do you know that you have got them all?'. This comes after, 'I can find some solutions' and 'I can recognise ones that are the same'. For example, is having sprinkles and sugar stars the same as having sugar stars and sprinkles on top of my iced biscuit?
Children are often quite good at having a random guess as to how to solve a problem. To become fluent at trial and improvement they need to be able to think about how to adapt their first guess so that it is more likely to become a solution rather than throwing the first one out and starting again. When starting to explore Dice in a Corner children may well put the dice together at random and be surprised when they get the magic total of 18. Those children who are becoming fluent at trial and improvement will then want to adjust the dice to see if they can make 18 in another way, rather than trying another random arrangement.
There are lots of NRICH problems that will help you develop these skills with children in our collections.
Being a competent and confident problem solver is central to the mathematical development of all our learners. It is also the major aim of the mathematics national curriculum in England. This article has detailed the individual elements that teachers can focus on to support children to gain this level of proficiency. We trust you will find it useful and we are always interested in your feedback and experiences as you explore problem solving together with the children in your class.
References
Primary National Strategy (2004) Problem solving A CPD pack to support the learning and teaching of mathematical problem solving. DfES Publications
Here is a pdf version of this article: DevelopingExcellenceInProblemSolving.pdf
Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Age 5 to 11
Published 2014 Revised 2019
Developing Excellence in Problem Solving with Young Learners
Becoming confident and competent as a problem solver is a complex process that requires a range of skills and experience. As teachers we can support this process in three principal ways:
- Through our choice of task
- Through structuring the stages of the problem-solving process
- Through explicitly and repeatedly providing children with opportunities to develop key problem-solving skills.
NRICH offers a wide range of rich tasks to engage learners in the problem-solving process. We want all our tasks to be used in such a way that they enable learners to explore and work from their own level of understanding, and then build on this towards new understandings. We believe that this approach offers the opportunity for rich, embedded learning.
Some of our NRICH tasks are simple games that can be played time and time again to develop numerical fluency as well as problem solving and reasoning, such as Spiralling Decimals and Totality (see also our article Developing Number Fluency - What, Why and How), whilst others may be non-routine problems that have a specific solution, such as Shape Times Shape. Some may take a short time, like Shut the Box, whilst others may intrigue and challenge over more than one lesson, like Dice in a Corner.
The key is to be clear how you want to use a particular problem to support the development of the children's skills to problem solve. It is tempting to choose a problem that relates to the mathematical content that you have been working on in class. However, whilst children need to be fluent with the mathematical content demands of any problem they tackle, it may be more productive to choose a problem that builds on a specific element of problem solving that you are working on as a class, and uses content that they are very familiar, and more confident, with.
The Primary National Strategy (May 2004) suggested that there are five different types of problem:
- Finding All Possibilities (for example Half Time)
- Logic (for example Teddy Town)
- Visual (for example Baravelle)
- Rules and Patterns (for example Ip Dip)
- Word Problems
The stages of the problem-solving process
The problem-solving process can usually be thought of as having four stages:
- Stage 1: Getting started
- Stage 2: Working on the problem
- Stage 3: Digging deeper
- Stage 4: Reflecting
We can helpfully spend time with children concentrating on one of these stages explicitly, in turn, as they learn to become confident problem solvers.
Stage 1: Getting started will mean offering them strategies to help them engage with the problem. These could be prompts such as:
- Tell me/a partner what you think the problem is about.
- What would help you understand the problem?
- You might like to draw a diagram, act it out or represent it with a model.
- Could you try something out and see what happens?
- What other problems have you seen that are 'a bit like' this one?
- What mathematical skills have you got that could be helpful here?
- Try making a simpler case to get an idea of how the problem works.
- Trial and improvement
- Working systematically (and remember there will be more that one way of doing this: not just the one that is obvious to you!)
- Pattern spotting
- Working backwards
- Reasoning logically
- Visualising
- Conjecturing.
The children will benefit from becoming proficient in each of these skills and working on one of them as a key focus in a lesson or series of lessons could be a useful strategy. Our article Using NRICH Tasks to Develop Key Problem-solving Skills offers further guidance.
Stage 3: Digging deeper usually happens when the problem has been explored and then it is possible to look for generalisations and proof. Here's an example from our NRICH problem Make 37:

Stage 4: Reflecting is the part of the problem-solving process where we support the children to:
- interpret their findings so far in the context of the problem
- explain their solution both verbally and in writing
- evaluate their method and compare different strategies.
Written recording could be in the form of a photograph, diagram or written explanation. Here are some children's solutions to our NRICH problem Domino Square that illustrate how recording may develop:



Children will need support to develop their proficiency with written recording. Here's an example of a child explaining their thinking for Eggs in Baskets. She has used a trial and improvement approach.

You can read more about types of recording in this article.
As children reflect on the problem-solving adventure, they will need to be supported to compare different strategies that were used to solve the problem in order to consider the efficiency of the method and the elegance of the solution. This will enable them to see how they might refine their own methods or adopt a different one next time they encounter a similar problem.
The skills needed for a problem-solving task
By this we mean the problem-solving skills listed above in Stage 2: working on the problem. It will help the children become fluent in these if you take every opportunity to explicitly talk about them and use the appropriate language when they occur in games or larger problem-solving activities. You may like to focus on developing one or two at a time. The article Using NRICH Tasks to Develop Key Problem-solving Skills unpicks what we mean by these skills and draws attention to activities which will help learners develop them.
Our youngest learners can start thinking about 'working systematically' in contexts such as choosing two toppings out of sprinkles, sugar stars or flakes to go on top of iced biscuits they are making. The key question is - 'how do you know that you have got them all?'. This comes after, 'I can find some solutions' and 'I can recognise ones that are the same'. For example, is having sprinkles and sugar stars the same as having sugar stars and sprinkles on top of my iced biscuit?
Children are often quite good at having a random guess as to how to solve a problem. To become fluent at trial and improvement they need to be able to think about how to adapt their first guess so that it is more likely to become a solution rather than throwing the first one out and starting again. When starting to explore Dice in a Corner children may well put the dice together at random and be surprised when they get the magic total of 18. Those children who are becoming fluent at trial and improvement will then want to adjust the dice to see if they can make 18 in another way, rather than trying another random arrangement.
There are lots of NRICH problems that will help you develop these skills with children in our collections.
Being a competent and confident problem solver is central to the mathematical development of all our learners. It is also the major aim of the mathematics national curriculum in England. This article has detailed the individual elements that teachers can focus on to support children to gain this level of proficiency. We trust you will find it useful and we are always interested in your feedback and experiences as you explore problem solving together with the children in your class.
References
Primary National Strategy (2004) Problem solving A CPD pack to support the learning and teaching of mathematical problem solving. DfES Publications
Here is a pdf version of this article: DevelopingExcellenceInProblemSolving.pdf

