Skip over navigation
Why do this problem?
The solution uses the formula for the area of a circle and gives practice in geometrical reasoning and manipulating algebraic expressions.
Possible approach
This printable worksheet may be useful: Salinon.
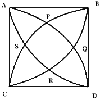
Start with a class discussion about the radii of the 4 semi-circles and the circle on AB as diameter. When the students have understood that there are only two unknowns involved, and the other radii can all be expressed in terms of the two unknowns, then they are ready to write down the areas and answer the question which they could do individually.
Dynamic geometry software could be a useful tool to aid investigation but this is not essential.
Key questions
If the blue semicircles have radii a and b what can you say about the other radii?
Possible support
Try Round and Round
Possible extension
Partly Circles is a similar problem.
Learners could make up their own problems of this type.


Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
Salinon
Age 14 to 16
Challenge Level 





- Problem
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources
Why do this problem?
The solution uses the formula for the area of a circle and gives practice in geometrical reasoning and manipulating algebraic expressions.
Possible approach
This printable worksheet may be useful: Salinon.
Start with a class discussion about the radii of the 4 semi-circles and the circle on AB as diameter. When the students have understood that there are only two unknowns involved, and the other radii can all be expressed in terms of the two unknowns, then they are ready to write down the areas and answer the question which they could do individually.
Dynamic geometry software could be a useful tool to aid investigation but this is not essential.
Key questions
If the blue semicircles have radii a and b what can you say about the other radii?
Possible support
Try Round and Round
Possible extension
Partly Circles is a similar problem.
Learners could make up their own problems of this type.
You may also like
Giant Holly Leaf
Find the perimeter and area of a holly leaf that will not lie flat (it has negative curvature with 'circles' having circumference greater than 2πr).
Quadarc
Given a square ABCD of sides 10 cm, and using the corners as centres, construct four quadrants with radius 10 cm each inside the square. The four arcs intersect at P, Q, R and S. Find the area enclosed by PQRS.
Get Cross
A white cross is placed symmetrically in a red disc with the central square of side length sqrt 2 and the arms of the cross of length 1 unit. What is the area of the disc still showing?

