Skip over navigation
Here is an interactive tool you can use to try out your ideas. Experiment with the sequences suggested in the problem (remember, $T$ is Twist and $R$ is Turn). What do you notice about the fractions that emerge?
To prove relationships generally, it may be helpful to use algebra.
For the final part of the task, it's useful to work backwards.
Consider the alternative function that maps $x \mapsto x-1$, an inverse twist.
Choose a fraction, and find a way to use the inverse twist and the turn functions to get back to zero.
How does that help you get from zero to your chosen fraction using the original twist and turn functions?
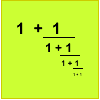
Or search by topic
Number and algebra
Geometry and measure
Probability and statistics
Working mathematically
Advanced mathematics
For younger learners
All Tangled Up
Age 14 to 18
Challenge Level 





- Problem
- Getting Started
- Student Solutions
- Teachers' Resources
Here is an interactive tool you can use to try out your ideas. Experiment with the sequences suggested in the problem (remember, $T$ is Twist and $R$ is Turn). What do you notice about the fractions that emerge?
To prove relationships generally, it may be helpful to use algebra.
For the final part of the task, it's useful to work backwards.
Consider the alternative function that maps $x \mapsto x-1$, an inverse twist.
Choose a fraction, and find a way to use the inverse twist and the turn functions to get back to zero.
How does that help you get from zero to your chosen fraction using the original twist and turn functions?
You may also like
There's a Limit
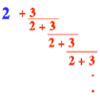
Explore the continued fraction: 2+3/(2+3/(2+3/2+...)) What do you notice when successive terms are taken? What happens to the terms if the fraction goes on indefinitely?
Not Continued Fractions
Which rational numbers cannot be written in the form x + 1/(y + 1/z) where x, y and z are integers?

